Deploying highly scalable cloud storage with Rook, Part 1 (Ceph Storage)
- By Gcore
- March 27, 2023
- 6 min read

It goes without saying that if you want to orchestrate containers at this point, Kubernetes is what you use to do it. Sure, there may be a few Docker Swarm holdouts still around, but for the most part, K8s has cemented itself as the industry standard for container orchestration solutions. As Kubernetes matures, the tools that embody its landscape begin to mature along with it. One of the areas we have seen some optimization, in particular, is in cloud-native storage solutions.
What is Rook?
Rook is an open-source cloud-native storage orchestrator, providing the platform, framework, and support for a diverse set of storage solutions to natively integrate with cloud-native environments.
It turns storage software into self-managing, self-scaling, and self-healing storage services. It does this by automating deployment, bootstrapping, configuration, provisioning, scaling, upgrading, migration, disaster recovery, monitoring, and resource management. Rook uses the facilities provided by the underlying cloud-native container management, scheduling, and orchestration platform to perform its duties. It supports a variety of different block, object, and file type storage.
Rook integrates deeply into cloud-native environments leveraging extension points and providing a seamless experience for scheduling, lifecycle management, resource management, security, monitoring, and user experience.
What is Ceph?
Ceph is a distributed storage system that is massively scalable and high-performing with no single point of failure. Ceph is a Software Distributed System (SDS), meaning it can be run on any hardware that matches its requirements.
Ceph consists of multiple components:
- Ceph Monitors (MON) are responsible for forming cluster quorums. All the cluster nodes report to monitor nodes and share information about every change in their state.
- Ceph Object Store Devices (OSD) are responsible for storing objects on local file systems and providing access to them over the network. Usually, one OSD daemon is tied to one physical disk in your cluster. Ceph clients interact with OSDs directly.
- Ceph Manager (MGR) provides additional monitoring and interfaces to external monitoring and management systems.
- Reliable Autonomic Distributed Object Stores (RADOS) are at the core of Ceph storage clusters. This layer makes sure that stored data always remains consistent and performs data replication, failure detection, and recovery among others.
To read/write data from/to a Ceph cluster, a client will first contact Ceph MONs to obtain the most recent copy of their cluster map. The cluster map contains the cluster topology as well as the data storage locations. Ceph clients use the cluster map to figure out which OSD to interact with and initiate a connection with the associated OSD.
Rook enables Ceph storage systems to run on Kubernetes using Kubernetes primitives. The following image illustrates how Ceph Rook integrates with Kubernetes:
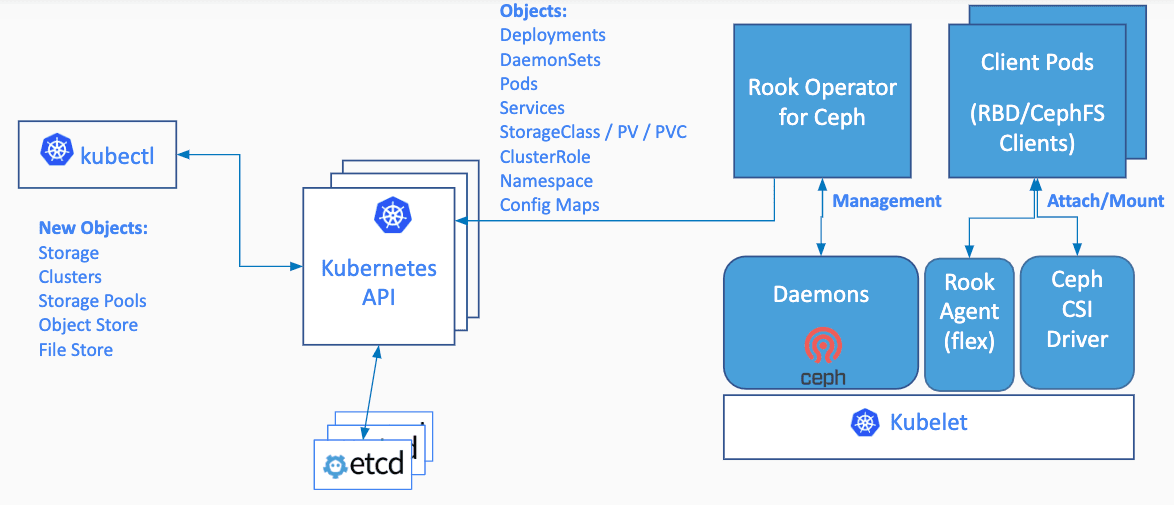
With Ceph running in the Kubernetes cluster, Kubernetes applications can mount block devices and filesystems managed by Rook, or can use the S3/Swift API for object storage. The Rook operator automates configuration of storage components and monitors the cluster to ensure the storage remains available and healthy.
The Rook operator is a simple container that has all that is needed to bootstrap and monitor the storage cluster. The operator will start and monitor Ceph monitor pods, the Ceph OSD daemons to provide RADOS storage, as well as start and manage other Ceph daemons. The operator manages CRDs for pools, object stores (S3/Swift), and filesystems by initializing the pods and other artifacts necessary to run the services.
The operator will monitor the storage daemons to ensure the cluster is healthy. Ceph mons will be started or failed over when necessary, and other adjustments are made as the cluster grows or shrinks. The operator will also watch for desired state changes requested by the api service and apply the changes.

The rook/ceph image includes all necessary tools to manage the cluster – there are no changes to the data path. Rook does not attempt to maintain full fidelity with Ceph. Many of the Ceph concepts like placement groups and crush maps are hidden so you don’t have to worry about them. Instead, Rook creates a much simplified UX for admins that is in terms of physical resources, pools, volumes, filesystems, and buckets. At the same time, an advanced configuration can be applied when needed with the Ceph tools.
Rook is implemented in Golang. Ceph is implemented in C++ where the data path is highly optimized. We believe this combination offers the best of both worlds.
Getting Started
This guide will walk you through the basic setup of a Ceph cluster and enable you to consume block, object, and file storage from other pods running in your cluster.
Minimum Version
Kubernetes v1.10 or higher is supported by Rook.
Prerequisites
To make sure you have a Kubernetes cluster that is ready for Rook, you can follow these instructions.
If you are using dataDirHostPath to persist rook data on Kubernetes hosts, make sure your host has at least 5GB of space available on the specified path.
TL;DR
If you’re feeling lucky, a simple Rook cluster can be created with the following kubectl commands and example yaml files. For the more detailed install, skip to the next section to deploy the Rook operator.
git clone --single-branch --branch release-1.2 https://github.com/rook/rook.gitcd cluster/examples/kubernetes/cephkubectl create -f common.yamlkubectl create -f operator.yamlkubectl create -f cluster-test.yamlAfter the cluster is running, you can create block, object, or file storage to be consumed by other applications in your cluster.
Production Environments
For production environments, it is required to have local storage devices attached to your nodes. In this walkthrough, the requirement of local storage devices is relaxed so you can get a cluster up and running as a “test” environment to experiment with Rook. A Ceph filestore OSD will be created in a directory instead of requiring a device. For production environments, you will want to follow the example in cluster.yaml instead of cluster-test.yaml in order to configure the devices instead of test directories. See the Ceph examples for more details.
Deploy the Rook Operator
The first step is to deploy the Rook operator. Check that you are using the example yaml files that correspond to your release of Rook. For more options, see the examples documentation.
cd cluster/examples/kubernetes/cephkubectl create -f common.yamlkubectl create -f operator.yaml## verify the rook-ceph-operator is in the `Running` state before proceedingkubectl -n rook-ceph get podYou can also deploy the operator with the Rook Helm Chart.
Create a Rook Ceph Cluster
Now that the Rook operator is running we can create the Ceph cluster. For the cluster to survive reboots, make sure you set the dataDirHostPath property that is valid for your hosts. For more settings, see the documentation on configuring the cluster.
Save the cluster spec as cluster-test.yaml:
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1kind: CephClustermetadata: name: rook-ceph namespace: rook-cephspec: cephVersion: # For the latest ceph images, see https://hub.docker.com/r/ceph/ceph/tags image: ceph/ceph:v14.2.5 dataDirHostPath: /var/lib/rook mon: count: 3 dashboard: enabled: true storage: useAllNodes: true useAllDevices: false # Important: Directories should only be used in pre-production environments directories: - path: /var/lib/rookCreate the cluster:
kubectl create -f cluster-test.yamlUse kubectl to list pods in the rook-ceph namespace. You should be able to see the following pods once they are all running. The number of OSD pods will depend on the number of nodes in the cluster and the number of devices and directories configured. If you did not modify the cluster-test.yaml above, it is expected that one OSD will be created per node. The rook-ceph-agent and rook-discover pods are also optional depending on your settings.
$ kubectl -n rook-ceph get podNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGErook-ceph-agent-4zkg8 1/1 Running 0 140srook-ceph-mgr-a-d9dcf5748-5s9ft 1/1 Running 0 77srook-ceph-mon-a-7d8f675889-nw5pl 1/1 Running 0 105srook-ceph-mon-b-856fdd5cb9-5h2qk 1/1 Running 0 94srook-ceph-mon-c-57545897fc-j576h 1/1 Running 0 85srook-ceph-operator-6c49994c4f-9csfz 1/1 Running 0 141srook-ceph-osd-0-7cbbbf749f-j8fsd 1/1 Running 0 23srook-ceph-osd-1-7f67f9646d-44p7v 1/1 Running 0 24srook-ceph-osd-2-6cd4b776ff-v4d68 1/1 Running 0 25srook-ceph-osd-prepare-node1-vx2rz 0/2 Completed 0 60srook-ceph-osd-prepare-node2-ab3fd 0/2 Completed 0 60srook-ceph-osd-prepare-node3-w4xyz 0/2 Completed 0 60srook-discover-dhkb8 1/1 Running 0 140sTo verify that the cluster is in a healthy state, connect to the Rook toolbox and run the ceph status command.
- All mons should be in quorum
- A
mgrshould be active - At least one OSD should be active
- If the health is not
HEALTH_OK, the warnings or errors should be investigated
$ ceph status cluster: id: a0452c76-30d9-4c1a-a948-5d8405f19a7c health: HEALTH_OK services: mon: 3 daemons, quorum a,b,c (age 3m) mgr: a(active, since 2m) osd: 3 osds: 3 up (since 1m), 3 in (since 1m)...Create a Block Storage
Block storage allows a single pod to mount storage. This guide shows how to create a simple, multi-tier web application on Kubernetes using persistent volumes enabled by Rook.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes a Rook cluster as explained in the Quickstart.
Provision Storage
Before Rook can provision storage, a StorageClass and CephBlockPool need to be created. This will allow Kubernetes to interoperate with Rook when provisioning persistent volumes.
Save this StorageClass definition as storageclass.yaml:
apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1kind: CephBlockPoolmetadata: name: replicapool namespace: rook-cephspec: failureDomain: host replicated: size: 3---apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1kind: StorageClassmetadata: name: rook-ceph-block# Change "rook-ceph" provisioner prefix to match the operator namespace if neededprovisioner: rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.comparameters: # clusterID is the namespace where the rook cluster is running clusterID: rook-ceph # Ceph pool into which the RBD image shall be created pool: replicapool # RBD image format. Defaults to "2". imageFormat: "2" # RBD image features. Available for imageFormat: "2". CSI RBD currently supports only `layering` feature. imageFeatures: layering # The secrets contain Ceph admin credentials. csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisioner csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: rook-ceph csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-node csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # Specify the filesystem type of the volume. If not specified, csi-provisioner # will set default as `ext4`. csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: xfs# Delete the rbd volume when a PVC is deletedreclaimPolicy: DeleteIf you’ve deployed the Rook operator in a namespace other than “rook-ceph” as is common change the prefix in the provisioner to match the namespace you used. For example, if the Rook operator is running in “rook-op” the provisioner value should be “rook-op.rbd.csi.ceph.com”.
Create the storage class.
kubectl create -f cluster/examples/kubernetes/ceph/csi/rbd/storageclass.yamlConsume the storage: WordPress sample
We create a sample app to consume the block storage provisioned by Rook with the classic WordPress and Mysql apps. Both of these apps will make use of block volumes provisioned by Rook.
Start Mysql and WordPress from the cluster/examples/kubernetes folder:
kubectl create -f mysql.yamlkubectl create -f wordpress.yamlBoth of these apps create a block volume and mount it to their respective pod. You can see the Kubernetes volume claims by running the following:
$ kubectl get pvcNAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESSMODES AGEmysql-pv-claim Bound pvc-95402dbc-efc0-11e6-bc9a-0cc47a3459ee 20Gi RWO 1mwp-pv-claim Bound pvc-39e43169-efc1-11e6-bc9a-0cc47a3459ee 20Gi RWO 1mOnce the WordPress and Mysql pods are in the Running state, get the cluster IP of the WordPress app, and enter it in your browser:
$ kubectl get svc wordpressNAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEwordpress 10.3.0.155 <pending> 80:30841/TCP 2mYou should see the WordPress app running.
If you are using Minikube, the WordPress URL can be retrieved with this one-line command:
echo http://$(minikube ip):$(kubectl get service wordpress -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}')NOTE: When running in a vagrant environment, there will be no external IP address to reach WordPress with. You will only be able to reach WordPress via the CLUSTER-IP from inside the Kubernetes cluster.
Moving On
Now that you’ve had a chance to play around a bit with using Rook with Ceph, let’s move on to the next part and learn how to set up Minio object storage with Rook!
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.