Encountering a 500 Internal Server Error indicates a server-related problem impacting website performance and user interactions. This blog post explains error 500’s impact on websites and user experience, root causes, troubleshooting steps for web visitors and site owners, and best practices to prevent future occurrences.
What Is a 500 Internal Server Error?
The 500 Internal Server Error is an HTTP status code that users may encounter while browsing websites. It indicates that the web server has encountered unforeseen issues with its configuration, application, or database, so it’s unable to fulfill the request made by the user’s browser. As a result, the page or something on the page won’t load.
The error originates from the website’s server infrastructure, not from the end user’s browser, computer, or internet connection. Users cannot resolve the issue themselves; the responsibility lies with the website administrators and server maintainers.
Different websites may present the message in various ways, including:
- 500 Internal Server Error
- HTTP 500 – Internal Server Error
- Internal Server Error
- HTTP 500 internal error
- That’s an error
- Error code 500
- 500 error
Implications of a 500 Internal Error
To understand why error 500 matters, let’s understand its three main implications.
1. Negative Customer Experience
The 500 Internal Server Error is a catch-all response, encompassing a wide range of underlying problems on the server. When visitors encounter a 500 Internal Server Error, its inherent lack of transparency can lead to frustration and dissatisfaction, significantly impacting the user experience and potentially even driving users away from the website. As an example, for e-commerce websites, an error 500 could result in lost sales.
To maintain a positive user experience and prevent traffic loss, administrators must promptly analyze server logs, review recent website changes, and run diagnostics to identify and rectify the server issue.
2. SEO Damage
500 Internal Server Errors can have adverse consequences for a website’s SEO performance. Search engines like Google and Bing consider user experience when ranking websites. Frequent Error 500s could signal an unstable or poorly maintained website, leading to a decline in search engine rankings. If the error affects pages linked by other websites, those inbound links may lose value, further impacting the site’s SEO.
3. Legal Implications
The 500 Internal Server Error carries potential legal implications. If critical information is inaccessible because of a 500 Error, such as access to terms of service agreements or privacy policies, these absences could lead to legal consequences. If the error occurs on e-commerce websites and results in lost sales and financial damages for third-party sellers, legal liabilities may arise.
How 500 Internal Server Error Looks
Let’s explore some common types of the 500 Internal Server Error and how they look on web browsers.
1. Generic Error Message

The most common form of the 500 Internal Server Error is the generic error message. Web servers display a standard error page that indicates an unexpected problem on their end. This generic response serves as a catch-all for various server-side issues. However, it lacks details about the root cause or nature of the problem.
2. Temporary Error (500)
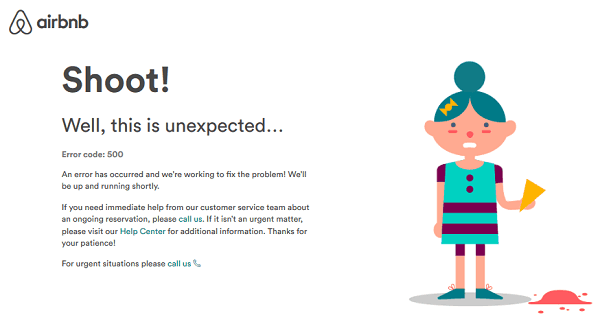
Some websites present a more user-friendly version of the 500 Internal Server Error as a “Temporary Error (500).” By using approachable language, this variation of the error message aims to reassure users that the problem is likely temporary. Friendly messaging can help ease users’ concerns and encourage them to try to access the desired page later.
3. Customized Error Messages

To ensure consistency with branding and user interface, websites have the flexibility to customize the appearance and wording of the 500 Internal Server Error message. Witty or funny messages, such as the one above, are intended to replace potential frustration with a smile.
4. Microsoft IIS-Specific Errors
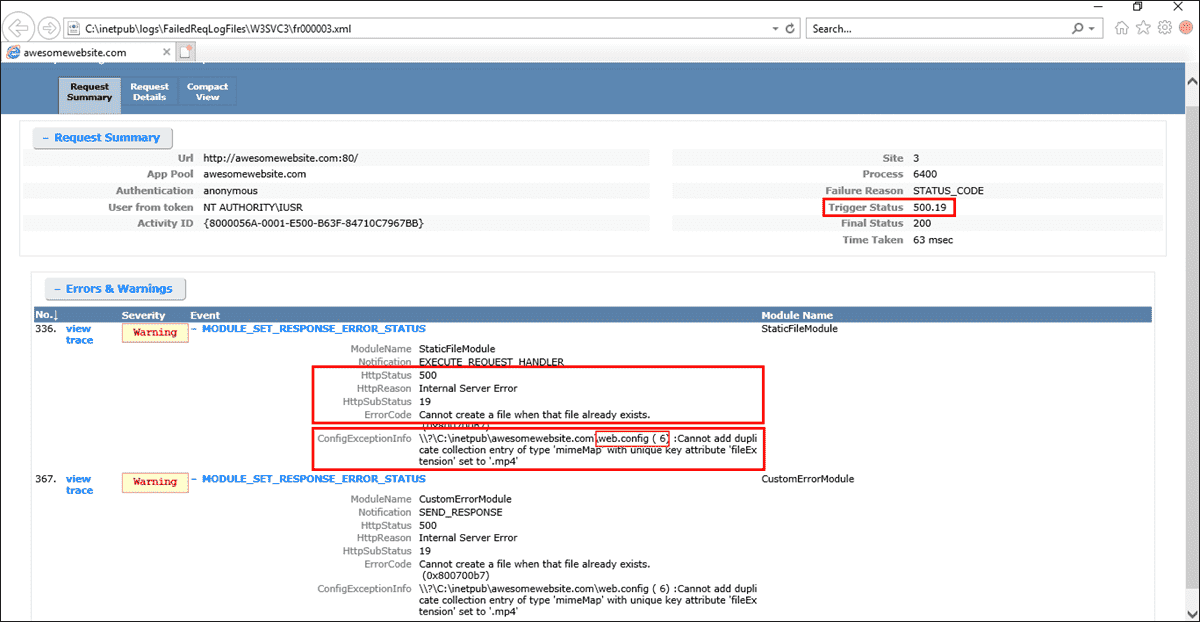
When the 500 Internal Server Error occurs on a website running Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS), users might encounter more specific error messages that offer insights into the server’s internal workings. Understanding these specific error codes helps website administrators and developers diagnose the root cause of the 500 Internal Server Error and implement appropriate fixes.
Microsoft IIS error codes are prefixed with “500,” followed by a dot and a specific number, each corresponding to different scenarios and conditions that the server encountered. For example, the “500.0” error indicates a problem with a module or ISAPI (Internet Server Application Programming Interface) on the web server, while the “500.12” error signifies that the application is in the process of shutting down.
How to Fix Error 500 as a Visitor
When encountering the HTTP 500 Internal Server Error as a web visitor, it is important to remember that the issue is not a result of your actions but originates from the web server hosting the website. However, before seeking further assistance, there are simple troubleshooting steps you can take to resolve the error and gain access to the website you’re trying to reach. Even if taking these actions does not resolve the issue, it can help you provide valuable information to the website administrators, making the resolution process smoother and more efficient.
- Reload or refresh the webpage
Start by refreshing the page, and if that doesn’t work, wait a few minutes and try again. Temporary server issues can sometimes cause the error, and website owners are often quick to resolve these problems.
- Take a break or restart your browser
Quit and reopen your web browser. If that fails, try restarting your computer. Sometimes, this simple step can bypass temporary issues causing the error.
- Clear browser cookies and cache
Over time, your browser accumulates temporary files like cookies and cache, which can interfere with the proper functioning of websites. Clearing these files can eliminate glitches and increase the chances of loading the page successfully. You only need to delete cookies associated with the error-prone webpage.
- Perform a status check with “Down for Everyone or Just Me”
If the error persists, you can use the service Down for Everyone or Just Me. Enter the website’s URL in the search field to determine if the problem is isolated to your device, or if the website is indeed experiencing issues.
- Contact the website’s owner
If all else fails, look for contact information on the website and get in touch with the website’s owner and/or administrator.
How to Fix Error 500 as a System Administrator
As a system administrator, by right troubleshooting steps you identify and resolve the issue causing error 500. Before diving in, it is essential to stress the importance of maintaining up-to-date backups. Having a reliable backup ensures that you can restore your system to a stable state if any unexpected issues arise during the troubleshooting process.
Here are twelve simple yet valuable troubleshooting methods that help system administrators tackle the 500 Internal Server Error:
- Resolve incorrect permissions on files and directories: Incorrect permissions can lead to the 500 Internal Server Error and can stop the server from executing scripts properly.
- Adjust Apache server timeout value to prevent errors: By modifying the Apache server timeout value in the
httpd.confconfiguration file, you can provide the server with more time to process requests, necessary for complex tasks or when temporary network issues occur.
- Check Apache and PHP error logs for valuable insights: Examine the error logs for any code or server failures that could be triggering the 500 error.
- Address errors in .htaccess files: A misconfigured
.htaccessfile can conflict with the web page you are trying to load, causing the 500 Internal Server Error. Check the.htaccessconfiguration for syntax errors and temporarily remove or rename the file to identify if it’s the cause of the error. - Ensure PHP setup is correctly configured: Exceeding the PHP memory limit can trigger the 500 Internal Server Error. Adjusting the
max_execution_timevalue in thephp.inifile can enable you to gain more memory for PHP processes. However, it is crucial to investigate and address the underlying cause of high RAM usage to ensure long-term website stability. - Verify compatibility of new software installations: When adding new third-party plugins, themes, or software to your website, compatibility issues may arise, leading to the 500 error. Regularly check for updates and ensure that all software is properly installed and up to date to prevent conflicts and improve website performance.
- Adjust server resource limits: Modify the
httpd.conffile to adjust the TimeOut directive, giving the server more time to complete tasks. Edit thephp.inifile to change values likememory_limitandmax_execution_timeto allocate more resources to PHP processes. Restart the server to apply changes. - Identify and rectify software conflicts: For Apache servers, you can disable modules using the
a2dismodcommand and enable them again witha2enmod. On nginx, commenting out lines in thenginx.confcan disable modules. After each change, restart the server and check if the error persists. Roll back changes as necessary. - Check for system overloads or attacks: Use monitoring tools like
toporhtopto inspect CPUs, memory, and bandwidth usage for signs of a denial-of-service (DoS) attack, which can cause error 500. Firewall configurations and intrusion detection systems like Fail2ban can offer additional layers of security. - Update software regularly: Employ package management tools like
aptoryumto update server software packages. Regularly run commands likeapt updateandapt upgradefor Debian-based systems, oryum updatefor Red Hat-based systems, to keep all software up-to-date. - Ensure database integrity: For MySQL databases, use commands like
CHECK TABLEorREPAIR TABLEto identify and fix potential issues. For PostgreSQL, thepg_dumpandpg_restorecommands can help backup and restore databases, ensuring data integrity. - Monitor hardware: Check hardware logs for any signs of failure, particularly focusing on RAM and hard disk states, and run hardware diagnostics regularly.
Best Practices to Prevent the HTTP 500 Internal Server Error
To maintain a smooth and hassle-free website experience, it’s important to adopt best practices that serve as preventive measures to help avoid the HTTP 500 Internal Server Error.
- Only use reputable plugins and themes from trusted sources. Regularly update and test plugins and themes to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Monitor website performance closely to identify and address all potential problems as soon as possible.
- Perform regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
- Back up your data regularly, so you can quickly restore your website in case of errors.
- Implement a web application firewall (WAF) to help prevent a range of attacks.
- Utilize monitoring tools to track website performance and detect errors early.
- Choose a reliable web hosting provider with the expertise to prevent HTTP 500 errors.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN) to enhance website performance and reduce the chances of errors.
- Implement error handling code and a logging system, like managed logging, to manage errors efficiently and identify their root causes.
Conclusion
The HTTP 500 Internal Server Error can be frustrating, but understanding its root cause and following simple troubleshooting steps can resolve the issue for web visitors and system administrators alike. Site owners should proactively implement preventative practices to minimize the chance of an error 500 occurring, ensuring optimized user experience.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.