Understanding and monitoring network socket connections is crucial for network administrators and Linux users. The ‘ss‘ command is a powerful tool that allows you to examine and manage socket connections on your Linux system. In this guide, we’ll delve into the ins and outs of using the ‘ss’ command to gain insights into your network connections and troubleshoot networking issues effectively.
What is Socket Connections?
Socket connections refer to the communication links established between two networked devices or processes. In networking, a socket acts as an endpoint for sending or receiving data across a computer network. Here are some key points about socket connections:
- Endpoint for Communication. A socket is an endpoint for network communication. It allows data to be sent and received between two devices or processes over a network.
- Unique Identifier. Each socket is identified by a combination of IP address and port number. This combination is unique, allowing data to be directed to the correct destination.
- Bidirectional Communication. Sockets enable bidirectional communication, meaning that data can flow in both directions, from the sender to the receiver and vice versa.
- Types of Sockets. There are various types of sockets, including TCP sockets (reliable, connection-oriented communication) and UDP sockets (unreliable, connectionless communication).
- Protocols. Different socket types use different communication protocols. For example, TCP/IP is commonly used for reliable socket communication, while UDP is used for applications where speed is more critical than reliability.
- Application Layer. Sockets are primarily used at the application layer of the OSI model, where application programs interact with the network for data exchange.
- Socket Programming. Developers use socket programming to create applications that can establish socket connections and exchange data over networks. This is common in client-server applications.
Understanding and monitoring socket connections is essential for network administrators and developers to ensure the proper functioning of networked systems. In the next section, we will explore how to examine socket connections.
Examining Socket Connections Using ss Command
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to examine socket connections using the “ss” command in Linux, complete with output and examples:
#1 Open Terminal
Open the Terminal application, which you can usually find in your Linux distribution’s application menu or access by using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Alt + T.
#2 Basic ss Command
To view a list of all socket connections on your system, simply run the following command:
ssSample Output:
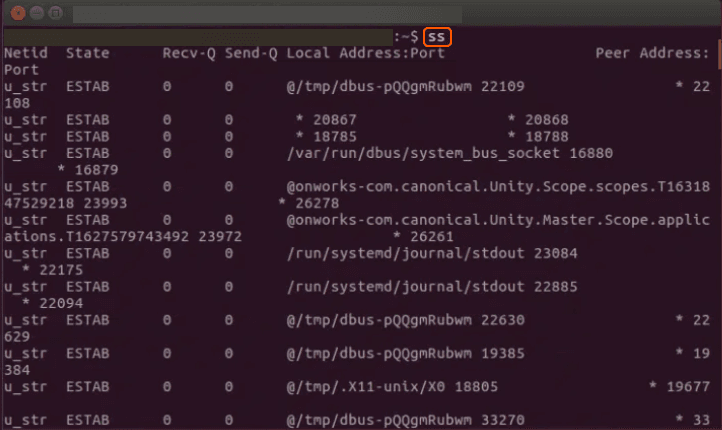
This command provides a list of established socket connections with details like the protocol, state, local address, and peer address.
#3 Display Listening Sockets
To see only the listening sockets (sockets that are waiting for incoming connections), use the “-l” option:
ss -lSample Output:

#4 Filter by Protocol
You can filter the results by protocol, such as TCP or UDP. For example, to view only TCP socket connections, use the “-t” option:
Sample Output:
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Porttcp ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.2:ssh 203.0.113.5:httptcp TIME-WAIT 0 0 192.168.1.2:3456 192.168.1.3:80#5 Display Process Information
To show the associated process information with each socket, use the “-p” option:
ss -t -pSample Output:
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Porttcp ESTAB 0 0 192.168.1.2:ssh 203.0.113.5:http users:(("sshd",pid=1234,fd=3))tcp TIME-WAIT 0 0 192.168.1.2:3456 192.168.1.3:80This command provides information about the associated process, including its name and process ID (PID).
#6 Filter by Port
To examine socket connections for a specific port, use the “-tuln” options followed by the port number. For example, to check port 80 (HTTP):
ss -tuln | grep 80Sample Output:
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:80 *:*#7 Advanced Filtering
You can use more advanced filtering options to narrow down the results based on various criteria such as state, local address, or peer address. For example:
ss -t state establishedThis command displays only established TCP connections.
Congratulations! You’ve now acquired the ability to utilize the ‘ss’ command for inspecting socket connections. This command, ‘ss,’ is a versatile and powerful tool for analyzing socket connections in Linux, offering valuable insights into network activities. Feel free to explore its various options and filters to cater to your specific monitoring requirements.
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.