NVIDIA L40S GPU Overview: Characteristics, Performance, AI Use Cases
- By Gcore
- March 21, 2024
- 6 min read

The new NVIDIA L40S is a formidable contender in the AI and graphics server marketplace. It’s a popular choice across industries and use cases for its power and performance, evidenced by long purchase wait times due to high demand. This high-performance computing solution is designed to handle generative AI, LLM training, and inference tasks with a moderate workload and low-precision arithmetic calculations. Additionally, its support for ray tracing means the L40S GPU can tackle tasks involving graphics-intensive workloads. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into how the L40S GPU performs on AI tasks compared to other NVIDIA options and identify the use cases for which it’s the optimal choice.
Why Performance Matters in AI
Training and inference, the most computationally demanding steps in an AI workflow, both require high-performance GPUs due to their complex calculations and large dataset handling. AI training involves teaching an AI system to understand and learn from the data provided to it. AI inference uses a trained model to analyze new data and produce new outputs. The superior parallel processing abilities of GPUs accelerate these tasks, significantly reducing training times and enabling rapid inference, essential for real-time applications.
As a high-performance GPU, the NVIDIA L40S delivers high throughput and low latency with maximum efficiency across use cases. We need to measure the performance of a GPU to see how it fits a particular use case. This means assessing its training time, power consumption, temperature, and GPU utilization, as well as the throughput and latency of the AI application.
With this understanding, let’s benchmark the L40S against two other high-performing NVIDIA GPUs, the NVIDIA A100 and H100, to explore the L40S’s efficiency and effectiveness across various demanding tasks.
L40S Performance Benchmarking
Benchmarking, a method for comparing the performance of one product with another, is helpful because it provides quick results and is simple to execute. In contrast to other evaluation methods, such as user reviews or theoretical analysis, it provides empirical data. It allows direct comparisons between NVIDIA’s L40S, A100, and H100. The MLPerf inference benchmark suite is a popular tool for measuring the speed at which a system can run models across diverse deployment scenarios.
How the L40S Stacks Up
In tests using this tool, the L40S relative performance is slightly weaker than the A100 on average, but when we compare the cost of each chip relative to its performance, the results for the L40S are noticeably stronger.
However, the H100 GPU outperforms the A100 and L40S by a factor of 2.3 to 2.5. This makes the H100 GPU best suited for AI tasks that involve building complex models from scratch, requiring high precision and extensive computational effort.
The NVIDIA H100 and A100 chips are priced at 4x and 2.6x the cost of the L40S, respectively—a significant price disparity, reflecting not just raw performance but also relative efficiency in handling complex AI workloads. The choice between these GPUs should thus consider both immediate budget constraints and the specific computational demands of the project.
In summary, if budget concerns are of primary importance, the NVIDIA L40S GPU is a solid choice for certain training and inference projects, including tasks involving the customization of existing trained models like OpenAI GPT, where the L40S offers sufficient performance at a more accessible price point. If absolute performance is the most important factor, the H100 is a superior choice.

L40S Use Cases
With this benchmarking in mind, let’s explore five use cases and see what the L40S’s potential is relative to other NVIDIA chip options.
AI Inference
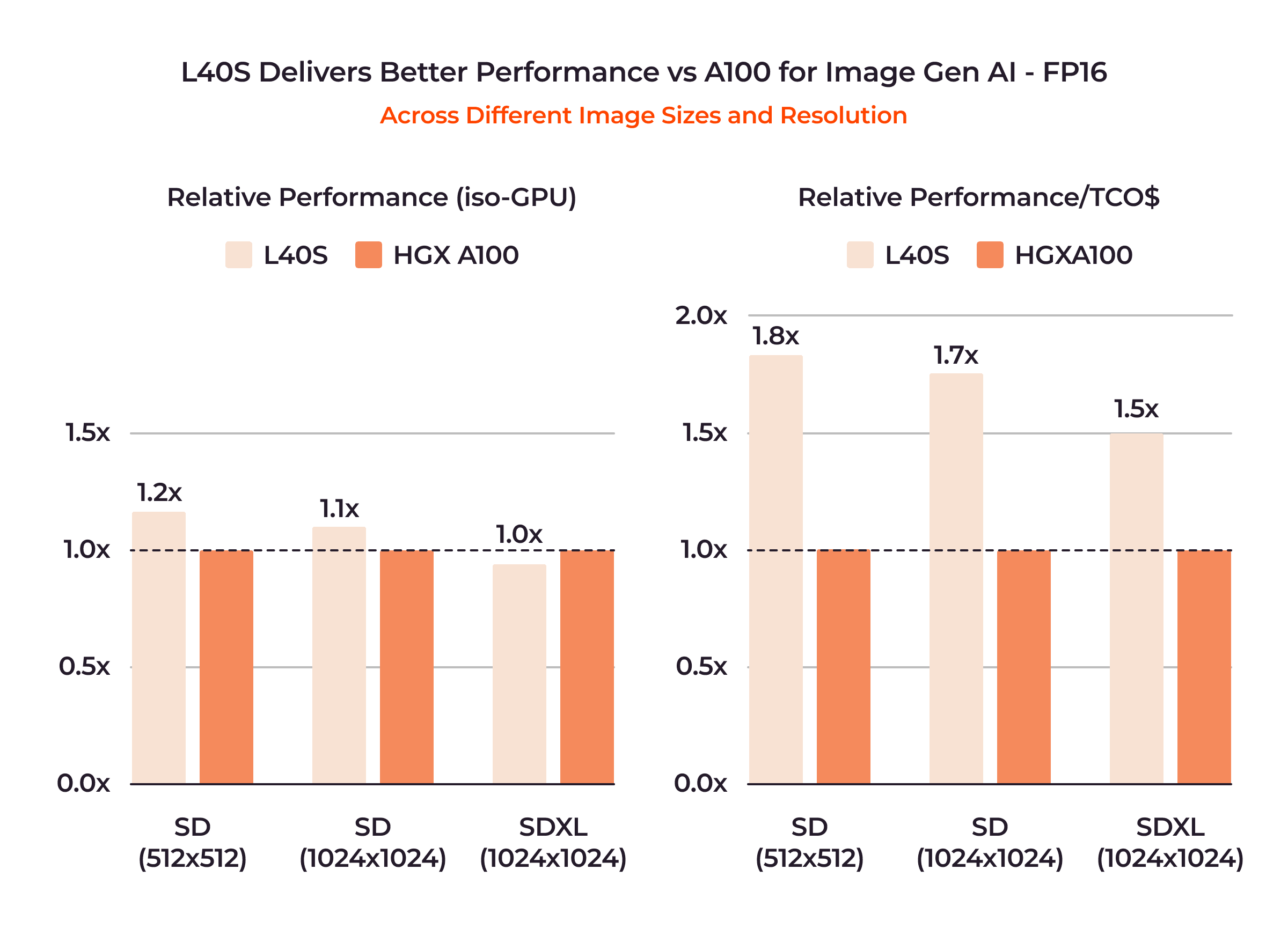
The NVIDIA L40S GPU, explicitly designed for AI inference tasks, achieves up to 1.5x greater inference performance than the A100 GPU. This enhancement is due to the use of Ada Lovelace Tensor Cores, which support fine-grained structured sparsity to boost inference speeds and employ 8-bit floating point (FP8) precision. FP8 precision allows for up to 4X higher inference performance compared to the previous generation GPUs. By opting for FP8 calculations over the more memory-intensive FP32 and FP64 formats, the Ada Lovelace Tensor Cores significantly reduce memory demands and enhance AI processing speeds.
The following performance results showcase how the L40S compares to the A100 across various deep learning models:

But the NVIDIA H100 GPU emerges as the top performer, delivering approximately twice the performance of the A100 for inference tasks using lower precision calculations (FP8 and FP16). This superior performance is attributed to the H100’s integration of a new FP8 data type, which significantly enhances calculation rates, quadrupling those of FP16 seen in the A100.

If you want the absolute top-performer GPU to run AI inference, the NVIDIA H100 is the one to go for. However, if you’re looking for a chip that provides a solid performance for AI inference tasks, comes with a more affordable price tag, and offers accessibility, the NVIDIA L40S is a better option.
High-Performance Computing
High-performance computing (HPC) refers to the technology capable of processing complex calculations at high speeds using clusters of powerful processors working in parallel. Regarding HPC processing improvement, the NVIDIA L40S GPU delivers up to 2.2 times the performance of the A100 GPU and the H100 GPU in simulation tasks using Altair nanoFluidX software, designed for complex workflow simulations in sectors such as automotive or aerospace.

Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses multi-layer neural networks for tasks using HPC technology. In deep learning tasks with FP32 (32-bit floating point in data representation where ultra-high precision isn’t crucial, the L40S chip often outperforms the A100 chip in computational performance.

Generative AI
In generative AI model training, the L40S GPU demonstrates 1.2 times the performance of the A100 GPU when running Stable Diffusion—a text-to-image modeling technique developed by Stability AI that has been optimized for efficiency, allowing users to create diverse and artistic images based on text prompts. However, the H100 GPU enhances performance by a factor of 1.25 compared to the L40S for the same task.

While both the L40S and the H100 GPUs deliver solid performance for generative AI training tasks, if the goal is to maximize performance for these tasks then the H100 GPU is the preferred choice. However, when considering the relative cost of the chips, the L40S delivers superior value.
AI Graphics
The NVIDIA L40S is designed to support graphics-related AI applications, such as interactive videos and AI-driven design and automation. It boasts advanced relevant inference capabilities, complemented by NVIDIA RTX™-accelerated ray tracing and specialized engines for encoding and decoding, enhancing a wide range of AI-powered applications in audio, speech, and video generation, in both 2D and 3D formats.
For professional visualization workflows demanding high fidelity—such as real-time rendering, product design, and 3D content creation—the L40S GPU is equipped with 142 third-generation Ray Tracing (RT) Cores and a substantial 48GB memory capacity, allowing it to deliver up to twice the real-time ray-tracing performance of the A100 and H100. Ray tracing, a technique for simulating scene lighting to produce physically accurate reflections, refractions, shadows, and indirect lighting, benefits from RT cores’ efficient operation, allowing rapid graphics rendering. Artists and engineers can craft immersive visual experiences and photorealistic content with remarkable speed. This, combined with its cost-effectiveness and reduced lead times, positions the L40S as the preferred choice for building AI models focused on image generation.
Scientific Simulations
The NVIDIA L40S is equipped with 18,176 CUDA® cores, giving it ample computational power for demanding workflows like engineering and scientific simulations. The L40S achieves single-precision floating-point (FP32) performance nearly five times that of the NVIDIA A100 GPU. This means the L40S can perform complex calculations and handle data-intensive tasks quickly, making it an excellent choice for researchers and engineers who require quick, accurate results from their simulations.
When Should You Not Use the L40S?
For certain use cases such as training complex AI models, the L40S might not be the best option. In this section, we’ll discuss scenarios where the L40S is potentially not the best choice, and what you should consider as an alternative.
Building Original Models
For building and training ML models from scratch, the H100 is the preferred GPU. It’s a high-end GPU designed for AI and machine learning workloads, featuring more CUDA cores, additional memory, and higher bandwidth than the L40S. These advantages make the H100 more capable than the L40S for these specific tasks.
GPU Clusters
If your objective is to create a GPU cluster, combining multiple GPUs to form a powerful resource for AI inference and modeling, you should consider the NVIDIA A100 or H100 GPUs instead of the L40S. These models support InfiniBand and NVLink technology, enabling effective GPU clustering for more demanding tasks. InfiniBand is a powerful new architecture designed to support I/O connectivity for internet infrastructure, thereby enabling high-speed communication between interconnected nodes. NVLink is a rapid GPU interconnect that connects two NVIDIA graphics cards.
While it is feasible to create GPU clusters using L40S GPUs, such clusters may not achieve the efficiency levels of A100 or H100 GPU clusters. This discrepancy is due to potential high latency and lower throughput, resulting from slower data transfer rates in L40S GPU clusters.
Conclusion
The NVIDIA L40S is ideally suited for training and inference for models that require specialized image processing and 3D graphics capabilities, thanks to its strong ray-tracing performance. It presents a cost-effective alternative, requiring a lower initial investment than its counterparts, the A100 and H100 GPUs. Despite the advantages of the NVIDIA L40S GPU, purchasing one is a significant investment and requires expertise to set up and maintain. It can also be challenging to assess whether the L40S aligns with the specific demands of your workload, especially when relying on general benchmarks.
We offer access to the industry-leading NVIDIA A100s and H100s through Gcore Edge AI GPU Infrastructure. Gcore Inference at the Edge, slated for launch in Q2 of 2024, will be powered by L40S chips, allowing you to benefit from the L40S capabilities in a simple and cost-effective way. We can help you determine the most suitable GPU for your AI or HPC workload.
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.