The Best Settings for YouTube Stream: Unleashing the Power of YouTube Studio
- By Gcore
- August 7, 2023
- 9 min read

YouTube, widely acknowledged as the most popular platform for live stream video content, stands out for its exceptional capabilities and service quality. With comprehensive stream settings, it offers users the opportunity to fully customize and enhance their viewer’s experience. However, these YouTube settings can be overwhelming, even for seasoned professionals. In this article, we will explain each setting in detail and determine the optimal configuration for your video stream.
Why Choosing the Best YouTube Live Streaming Settings Matters
Before delving into the intricacies of specific YouTube settings, it is crucial to understand their importance. Why are these settings for YouTube streaming so important?
First, viewers demand exceptional video quality. Poorly optimized settings can result in subpar content that fails to meet audience expectations. However, excessively high settings across the board may lead to buffering issues or render the stream unwatchable. Choosing “the best” streaming settings is aimed at achieving optimal performance.
In addition to considerations of quality and speed, many other factors come into play when determining ideal streaming parameters, including the type of video camera used and the target devices of the intended audience. This article will help you to identify the YouTube stream settings that align with your unique requirements and circumstances.
Understanding Live Settings in Tab “Stream Settings”
The key parameters for a YouTube stream can be found in the tab “Stream Settings” in YouTube Studio’s “Stream” tab. Before exploring the specific values to input, it is important to understand how YouTube streaming works.
How YouTube Streaming Works
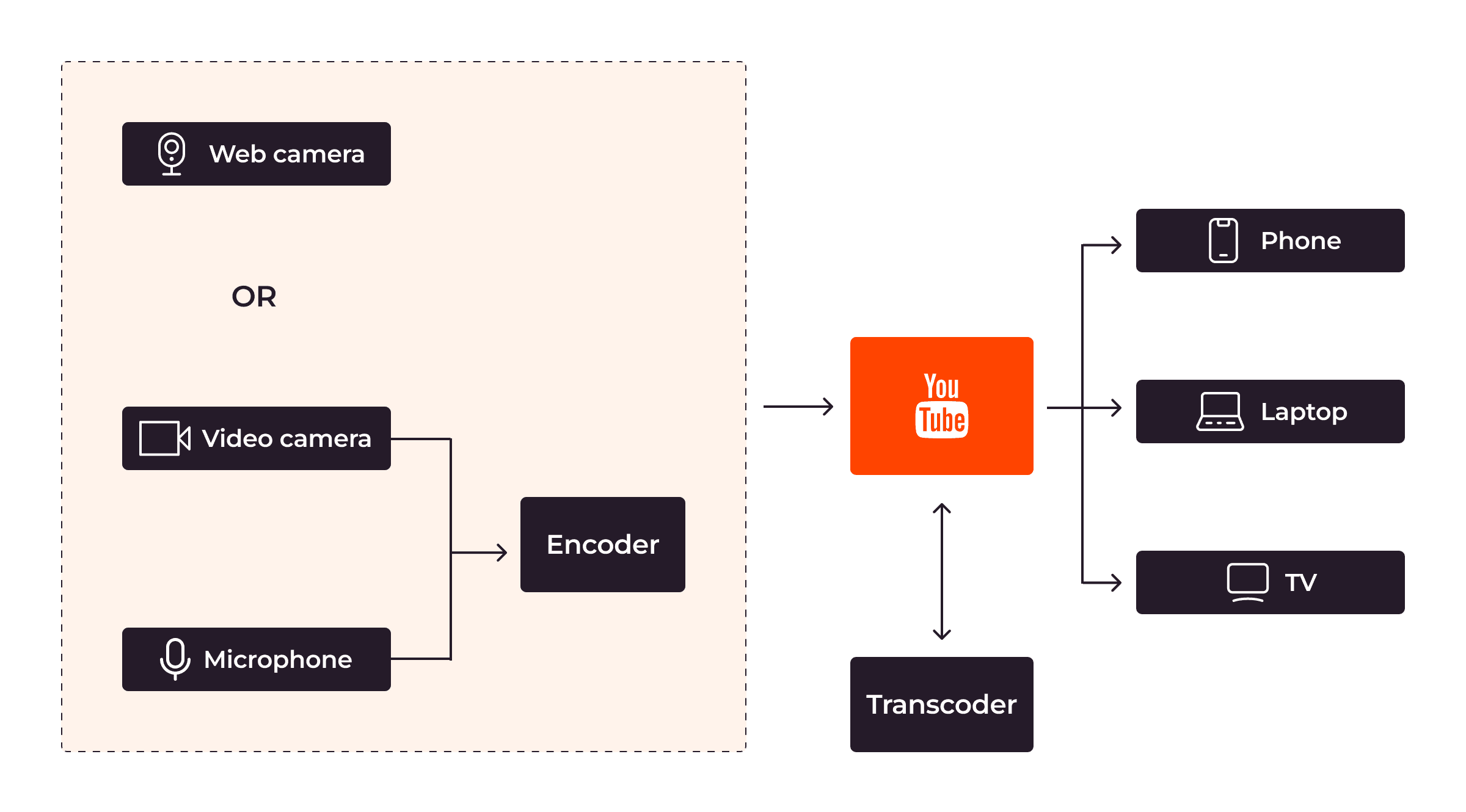
To generate video content, creators rely on dedicated video and audio capture hardware. This can range from a built-in webcam on your laptop to a cutting-edge professional video camera accompanied by a suite of high-quality microphones, enabling the creation of immersive surround audio tracks.
The media captured is transmitted to YouTube through one of two protocols: RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol) or HLS (HTTP Live Streaming). While video captured with a web camera can be delivered directly to YouTube, professional-grade equipment necessitates the use of an encoder to transmit the captured media to YouTube Studio.
Once YouTube receives the video, it undergoes transcoding, a process that converts the video into various supported resolutions. The transcoded video is then disseminated to viewers, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of devices and optimizing the viewing experience.
What Is a “Stream Key”?
When it comes to more advanced streaming setups, simply relying on a built-in web camera may not suffice. In such cases, your equipment needs to be properly configured to transmit content to YouTube using a unique identifier known as a “stream key.”
The stream key, in conjunction with the stream URL, serves as your credentials, granting your encoder access to your dedicated streaming channel on YouTube. It establishes a secure and exclusive connection between your encoding hardware and YouTube’s streaming platform.
RTMP/RTMPS
By default, YouTube uses the RTMP protocol for streaming. While RTMP is suitable for video streams, it may not provide optimal security measures. Content creators can enhance security for streams by implementing encryption.
YouTube offers an extension to RTMP called RTMPS, which stands for RTMP Secure. RTMPS leverages a TLS/SSL (Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer) connection to encrypt your stream, ensuring the privacy and authenticity of the content received by your viewers.
Enabling RTMPS is a straightforward process. In your stream settings, you will find a lock icon located near the stream URL. By clicking on this icon, the URL will automatically change to one that begins with “rtmps,” indicating that your stream is now utilizing the secure RTMPS protocol.
Encoding and Video Quality
When determining the appropriate encoding parameters for your stream, it is important to consider two key factors: achieving optimal video and audio resolution while ensuring a stable streaming experience. These two factors often require trade-offs, and your goal is to find the right balance between them.
To begin, assess your hardware’s uploading capabilities through a speed test. This test will reveal the maximum upload speed your connection can reliably sustain, enabling you to select suitable encoder settings. For example, streaming a video at 1080p resolution with 60 frames per second (fps) typically requires a stable upload speed of up to 9 Mbps. Therefore, if your speed test indicates a consistent speed of 11 Mbps, you can confidently stream at 1080p 60 fps.
However, it is important to note that speed requirements are not set in stone and can vary depending on multiple factors. For example, dynamic video content may require a higher bitrate. Consequently, it is advisable to leave some headroom for bitrate fluctuations and connectivity irregularities by choosing slightly lower encoding settings than your current upload speed allows. YouTube provides bitrate ranges for each supported resolution and fps, which can aid you in making informed decisions. These ranges can be found here.
Bitrate
By default, YouTube’s settings are configured to receive a variable bitrate (VBR) stream. This recommended option allows YouTube to automatically detect the stream’s bitrate, frame rate, and resolution. VBR is particularly beneficial for dynamic videos as it adapts to the varying volume of data in each video segment, maintaining consistent visible quality throughout.
If you prefer to have more control over the bitrate and more predictability in connectivity requirements, you can create a new stream key and enable manual settings. This approach is especially relevant for static video content that doesn’t exhibit frequent fluctuations in visual complexity.
Latency
Latency refers to the time interval between capturing your content and delivering it to your viewers.
Lower latency enables enhanced synchronization between the presenter and the audience, enabling real-time interaction. However, it’s important to note that lower latency can result in increased buffering on the viewer’s side. If real-time interaction is a critical aspect of your stream, it is essential to ensure a reliable internet connection and fine-tune your encoding parameters to align with the available bandwidth. Conversely, if live interaction is not a requirement, opting for higher latency provides a more stable and consistent streaming experience.
YouTube supports three levels of latency: normal, low, and ultra-low. Choosing the appropriate latency level depends on your specific needs. Normal latency prioritizes stream reliability, while low and ultra-low latency options prioritize real-time engagement and interaction with the audience.
Digital Video Recorder (DVR) Technology
DVR allows your viewers to pause, rewind, and continue watching your stream from any moment. This feature adds an extra level of convenience for your audience, even though utilizing DVR functionality means sacrificing a portion of the real-time component of the streaming experience.
Enabling or disabling DVR functionality is a straightforward process. Simply toggle the “Enable DVR” switch in the stream settings to activate or deactivate this feature. It’s important to note that if you choose to enable DVR during the streaming session, the new settings will only apply to individuals who join the stream after the changes are made.
YouTube’s DVR functionality has certain limitations. Users are typically able to rewind a limited amount of time within your video stream, which is dependent on factors such as latency and the viewer’s device. However, these limitations are typically measured in hours, and in most cases, they provide ample flexibility for viewers. Additionally, disabling DVR is not possible for web and mobile cameras, as these devices inherently support continuous streaming without the ability to pause or rewind.
360° Video
YouTube supports providing your audience with a 360° video experience, also known as immersive or surround video. However, it is important to note that, at the time of writing, YouTube displays 360° videos in an equirectangular projection format. To enable this feature, simply toggle the “360° video” switch in stream settings.
When streaming immersive videos, it’s crucial to consider the impact on connectivity. These types of videos demand more robust and stable internet connections to ensure a seamless viewing experience. To achieve optimal results for 360° video content, it is recommended to use at least the 1440p resolution with a 16:9 aspect ratio.
Delay
In addition to managing latency, content creators can configure an artificial delay for your stream of up to one minute. This feature holds particular significance in scenarios such as live gaming streaming, where implementing a delay can make it more challenging for other players to track your presence on the game map. By configuring an artificial delay, you add an extra layer of privacy and strategic advantage to your gameplay.
Closed Captions
YouTube supports captions, which can be embedded in the video by your encoder or sent separately via HTTP by special software. In addition to these options, YouTube offers automatic caption generation or streams where sophisticated equipment is not utilized and the primary language spoken is English. This feature automatically generates closed captions for your stream, enhancing accessibility and allowing a broader audience to engage with your content. To enable automatic captions, simply select Automatic captions in the “Captions source” field within your stream settings.
Optimal Live-Streaming Settings for YouTube
Taking into account the information provided above, selecting the optimal YouTube live-streaming settings involves a systematic approach. The key considerations are:
- Measure connectivity: Begin by evaluating your internet connection and conducting a speed test. This will provide valuable insights into your uploading capabilities. Refer to YouTube’s recommended bitrate ranges, available on this YouTube help page, to determine the suitable settings. For example, a stable upload speed of 15 Mbps enables safe streaming at 1440p with 30 fps.
- Assess target devices: Understand the primary devices your audience uses. If they predominantly view content on larger screens, but your upload speed limits you to 720p resolution, it may be necessary to explore options to improve your bandwidth or consider alternative streaming resolutions.
- Experiment and test: Before going live, it is advisable to experiment with different combinations of settings using recorded videos. This allows you to assess the effectiveness of various configurations and identify the settings that work best for your specific case. By conducting thorough testing, you can refine and optimize your live-streaming settings.
Best Encoders and Encoder Settings to Stream RTMP Stream
It is always possible to stream content captured by a built-in or external web camera directly. However, when streaming advanced content, using an encoder becomes crucial as a webcam may not suffice. Encoders play a pivotal role in converting video content into a digital format suitable for streaming on YouTube. They can be either software applications or standalone hardware devices like video cameras and microphones.
Encoders for YouTube Stream
YouTube certifies encoders that adhere to best practices and recommendations, ensuring an optimal user experience for streamers. Some of the popular YouTube-verified software encoders include Cinamaker Director Studio and Streamlabs. Notable hardware encoders include LiveU Solo and NVIDIA GPUs equipped with NVENC, a powerful hardware encoder. The full list of certified encoders can be found on YouTube’s official website.
Encoder Settings for YouTube Stream
YouTube supports the H.264 video codec (also known as AVC or MPEG-4 Part 10) as the standard for RTMP streaming. Video bitrate and frame rate should be configured based on the recommendations discussed in previous sections.
Regarding audio, you have the option to choose between MP3 or the more advanced AAC codec for 5.1 surround sound.
| Audio type | Stereo | 5.1 |
| Codec | MP3 | AAC |
| Bitrate | 128 Kbps | 384 Kbps |
| Sample rate | 44.1 KHz | 38 KHz |
YouTube has gathered a complete list of recommended encoder settings in the table at the end of this article.
Recommended Advanced Settings
In this section, we will explore advanced options that can elevate the quality and experience of your professional video content.
High Dynamic Range (HDR)
You can stream HDR video via YouTube. HDR technology enhances videos by making them more realistic, dynamic, and vivid.
To enable HDR streaming, ensure that your video camera and encoder support HDR output. In YouTube stream settings, create a new stream key with the “Turn on manual settings” option disabled and select the HLS protocol.
It is important to note that HDR is only supported over HLS. HLS is a different protocol than RTMP and has a higher latency. At this time, YouTube does not support HDR via RTMP.
5.1 Audio
Capturing 5.1 audio requires professional and potentially expensive equipment. However, if your aim is to target TV devices, YouTube to detect your 5.1 audio track can provide an immersive audio experience on TV surround sound systems.
To enable YouTube to detect your 5.1 audio track, create a new stream key with the “Turn on manual settings” option unchecked to allow YouTube to recognize and process the 5.1 audio track.
Noise Reduction
While not directly related to YouTube, minimizing background noise is crucial for high-quality audio. Consider the following tips:
- Record in a quiet environment to minimize external disturbances.
- Utilize professional high-end microphones that offer superior noise-canceling capabilities.
- Position the microphone at the optimal distance from the sound source, as specified in the microphone’s manual.
- Use noise suppression software or hardware to further reduce unwanted background noise.
- Alternatively, incorporate background music to help mitigate the presence of any remaining background noise.
How To Check “Stream Health”
Once the stream has been configured and broadcasting content to viewers has commenced, YouTube provides a “Stream Health” tab where you can monitor the status and performance of your ongoing stream.
Within the “Stream Health” tab, YouTube generates log messages that provide information about the current state of your stream. If everything is functioning smoothly, you will see a message indicating that your stream is healthy. In cases where there is room for improvement, you will receive an “OK” status with recommendations on how to enhance your viewers’ experience. For example, YouTube may suggest adjusting the resolution or bitrate settings to optimize stream quality.
If issues arise during streaming, YouTube will alert you with a message highlighting the poor health of your stream in red. Accompanying log messages will provide details about the specific issue causing the poor stream health. For instance, if there is a connectivity outage or insufficient data being received by YouTube, your viewers may experience frequent buffering during playback.
Streaming to Other Platforms
While YouTube offers a fantastic platform for your video content, it is not the sole option available to reach your audience. At some point, you may wish to expand your viewership by streaming on other popular video streaming services like Twitch or Facebook. However, managing multiple streams across different platforms can quickly become complex and resource-intensive.
Gcore provides a simple solution to this challenge. By streaming to Gcore, you gain the ability to effortlessly restream your content to a variety of services without the need for complicated equipment configurations. All you have to do is provide Gcore with the necessary stream keys and URLs when setting up your streaming configuration. Gcore offers the flexibility to restream your content to an unlimited number of services, allowing you to reach a wider audience across multiple platforms simultaneously.
Conclusion
This article has provided comprehensive insights into various aspects of YouTube streaming and video streaming generally, guiding you in selecting optimal parameters to ensure a standout streaming experience. By considering factors such as connectivity, encoding settings, latency, closed captions, and advanced features like HDR and 5.1 audio, you can elevate the quality and engagement of your streams. As you continue your streaming journey, remember that optimizing your settings, leveraging advanced features, and choosing the right platform can significantly impact the success of your streams. Embrace the possibilities and deliver exceptional streaming experiences to captivate and engage your viewers.
If you’re looking to expand your streaming reach to multiple platforms or seeking an advanced platform that caters to your specific requirements, Gcore offers a solution. With Gcore, you can easily restream your content to various platforms, simplifying your workflow and reaching a broader audience. To explore Gcore’s offerings and learn more about how it can enhance your streaming endeavors, visit their website for further information.
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.