Error 404 is an HTTP status code that signifies a server’s inability to retrieve requested web content due to various reasons, such as inaccurate URLs, broken links, or DNS issues. This article is a guide to understanding 404 errors: what they are, why they matter, and how to resolve and prevent them. You’ll learn about the architecture of 404 errors and the impact they have on websites, businesses, users, and customers. Most importantly, you’ll come away with proactive strategies for resolving 404 errors, both as an administrator and as a user.
What Is Error 404?
Error 404 occurs when users try to access a web page that doesn’t exist. The web page could be a nonexistent URL, deleted page, or broken link, among other causes. Users experience frustration when the expected web page doesn’t load and instead this error is shown, so website owners must proactively address this issue through continuous monitoring to avoid Error 404 occurrences, and by offering user-friendly solutions in the event of 404 errors.
The wording of the error message may differ slightly based on the browser in use and the nature of the missing resource. Common variations of the Error 404 include:
- 404 not found
- HTTP Error 404
- HTTP 404
- 404 Error
- 404
- Page not found
- Error 404. The page you’re looking for can’t be found.
- 404 File or Directory Not Found
Sometimes, web browsers display an HTML page that describes the error. This message informs the user about the encountered problem and may suggest potential solutions or alternative routes to access the intended web page.
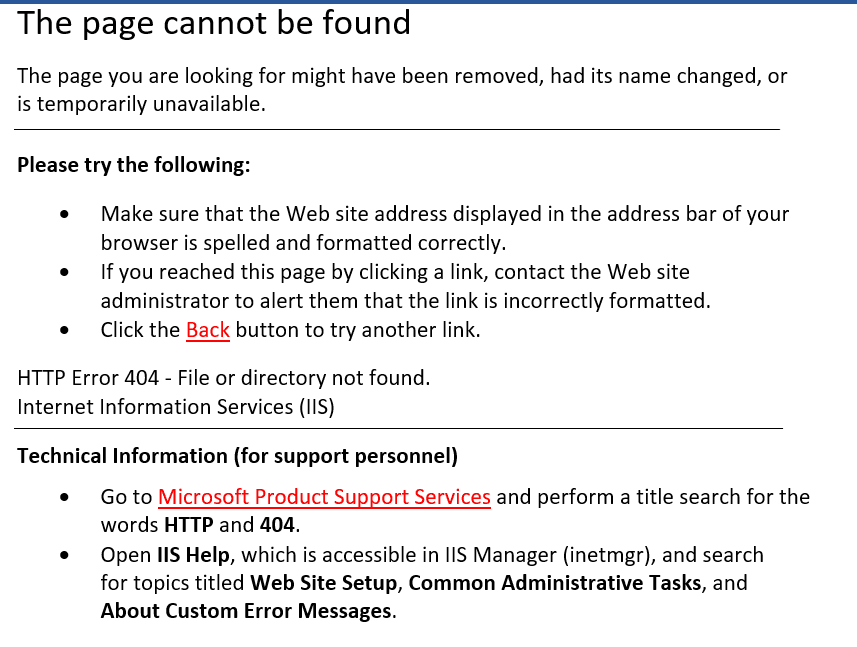
What Causes a 404 Error?
Error 404 may occur for a variety of reasons, including:
- Nonexistent page: Attempting to access a page that doesn’t exist, perhaps because it has been deleted or relocated to a new URL
- Inaccurate inbound links: Relatedly, outdated or incorrect inbound links can direct users to pages that don’t exist, whether because the page has been deleted, relocated, or simply due to a typo in the link
- Incorrect URL: Inputting an incorrect URL, for example with a typo
- Missing assets: The absence of critical web assets, such as files, CSS stylesheets, JavaScript files, or other fundamental components necessary for proper website functioning
- Server malfunction: A malfunctioning server may be unable to process the request for a web page correctly
- DNS settings: Incorrect DNS (Domain Name System) settings can lead to the inability to resolve the requested domain or URL
- Domain propagation: When a domain is still in the process of propagating across the internet, it may result in temporary accessibility issues
- Misconfiguration: Misconfiguration of server settings or website parameters
- File permissions: Incorrect file permissions on the server can restrict access to certain files
- Site operations: During website migration, routine maintenance, or when a server experiences technical problems, Error 404 may surface as a temporary inconvenience
- Browser cache: In situations where a browser has cached a previous version of a page that resulted in an Error 404, subsequent attempts to access the page may yield the same error until the cache is cleared
What Is The Impact of Error 404?
The impact of Error 404 on a website can be significant, affecting both user experience and the website’s overall performance:
User Frustration and Loss of Trust
Error 404 messages can frustrate website visitors and cause them to lose trust in the website and its content. Frustration is a natural response when the expected web page doesn’t appear. Users may perceive it as a sign of poor website maintenance or an unreliable organization, which can lead to a negative impression of the business or brand associated with the site. For example, users may not trust information from a site with 404 errors. Ultimately, visitors may abandon the website due to frustration or lack of trust, leading to potential losses in conversions and engagement.
SEO Impact
While typing an incorrect URL typically triggers an Error 404, it does not inherently affect SEO rankings. However, when these errors occur due to broken links or missing pages within a website, it can have a detrimental impact on SEO. Search engines prioritize websites with well-structured, accessible content. Unreachable or dead-end pages hinder effective website crawling, preventing search engines like Google or Bing from discovering and indexing all the website’s pages. This, in turn, can negatively affect the website’s SEO performance.
Reputational Damage
Accumulating a high number of Error 404 on a website can harm its reputation in the eyes of both users and search engines. It suggests a lack of attention to website maintenance and can diminish the site’s credibility with users and algorithms alike.
Bounce Rate
Search engines, such as Google, track user interactions with websites, including the time spent on a page. When users encounter an Error 404 and promptly leave the website or click the back button, it results in a high bounce rate. A high bounce rate can signal to search engines that the website does not provide the content or resources users are seeking. Consequently, search engines may lower the website’s ranking in Search Engine Results Pages (SERP,) making it less visible to potential users.
How to Identify Pages and Links With 404 Errors
Identifying and addressing 404 errors is essential for ensuring a positive online experience for users and optimizing your SERP ranking for SEO. Depending on the size of your website, you can employ different methods and tools to efficiently detect these errors.
Manual Checks for Small Websites
For smaller websites, website owners or administrators can manually check for 404 errors by navigating through all pages and links on the site. This involves clicking on each link and verifying that they are live and lead to the intended content. While this method is feasible for small websites, it becomes impractical for larger sites with hundreds or thousands of pages since a page may be missed out and it would require excessive human time and effort.
Automated Tools for Large Websites
Since manual checks are not feasible for extensive websites with numerous pages and files, administrators can instead utilize various automated tools to identify broken links and unreachable pages. Some popular options include:
- Google Search Console: This free tool offers an in-built crawler that can detect broken links. After submitting your website to Google Search Console, it will periodically crawl your site and compile a list of pages with issues, including 404 errors. This valuable data helps you pinpoint and address these problems efficiently and effectively.
- Bing Webmaster Tools: If your website is registered with Bing Webmaster Tools, you can use it to identify pages with 404 errors. Simply log in to your Bing account, navigate to the SEO section, and access the SEO reports. Any pages with 404 errors will be listed under the HTTP 400–499 errors category.
- Dead link checker: This tool is specifically designed to identify broken links on your website and helps you to fix them efficiently.
- W3C link checker: W3C’s tool tests and identifies broken pages within your website and also verifies outgoing links to other external websites, ensuring a comprehensive assessment of your site’s links.
- Premium audit tools: Consider using comprehensive audit tools such as Ahrefs or Sitechecker. These tools offer advanced features for monitoring your website consistently, and can alert you immediately when 404 errors or other issues are detected.

How To Fix 404 Errors
How you fix a 404 Page Not Found error depends on whether you are a website visitor or the website owner/administrator. Let’s look at both situations.
How Can Website Visitors Fix 404 Errors?
There are various steps website visitors can take to fix an Error 404 Not Found:
- Reload the page: Sometimes, an Error 404 may occur due to a temporary issue with the page or a momentary connection problem. Simply try reloading the page by clicking the refresh button on your browser. This action can often resolve the issue if it’s transient.
- Clear browser cache: Your browser may have cached a page that has since been deleted, moved, or updated. Clear your browser’s cache to ensure you are viewing the most current version of the webpage.
- Check the URL: Ensure that you have entered the correct URL. Mistyped URLs are a common cause of 404 errors.
- Use a search engine: If you suspect that the URL you have is incorrect or outdated, you can use a search engine to find the page. Enter the website’s name along with relevant keywords to search for the specific page you’re looking for.
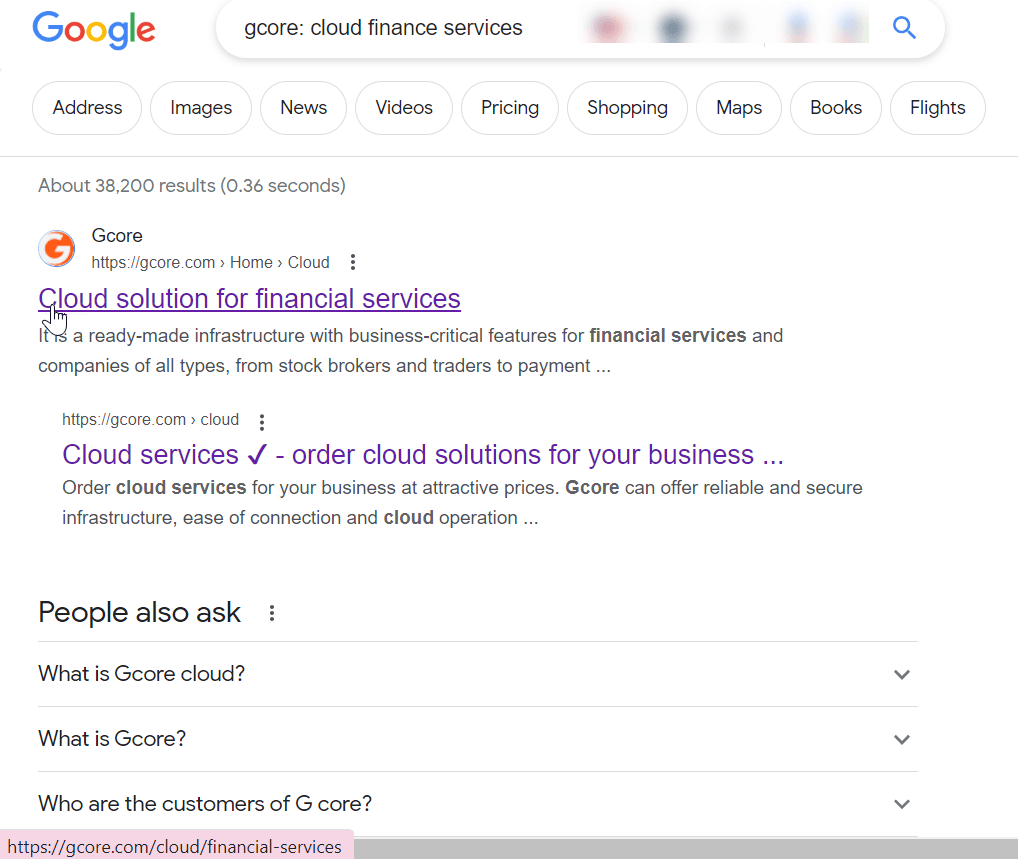
For example, if you encounter a 404 error while trying to access the Cloud For Financial Services page on the Gcore website, you can search on Google using a query like gcore: cloud financial services to locate the correct URL. To search for pages on a specific website, use the site:websiteURL query format, such as site:gcore.com cloud financial services.
- Contact website administrator: If you are unable to resolve the issue through the above steps, consider reaching out to the website administrator. They can provide information on whether the page or file still exists, has been moved to a different location, or if there are any issues with accessing it. The website administrator can help you find the desired content.
These steps empower website visitors to troubleshoot and potentially resolve 404 errors, providing a smoother browsing experience.
How to Fix Error 404 as an Admin or Website Owner?
Fixing Error 404 as an admin or website owner involves taking a number of steps and implementing strategies to ensure a smooth user experience and maintain the integrity of your website. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to address Error 404:
- Identify and document 404 errors. Use tools like Google Search Console, Broken Link Checker, or similar utilities mentioned above to identify all pages or assets on your website that are generating 404 errors. Keep a record of these errors for reference.
- Prioritize fixes. Focus on addressing errors that have the most significant impact on user experience, such as critical pages or frequently visited content. Some minor 404 errors may not require immediate attention.
- Confirm DNS configuration. Use online tools like DNSMap, DNS Checker, or whatsmydns.net to verify that your domain is correctly pointing to the appropriate hosting server. Ensure that DNS settings are correctly configured, especially after server migrations or DNS changes.
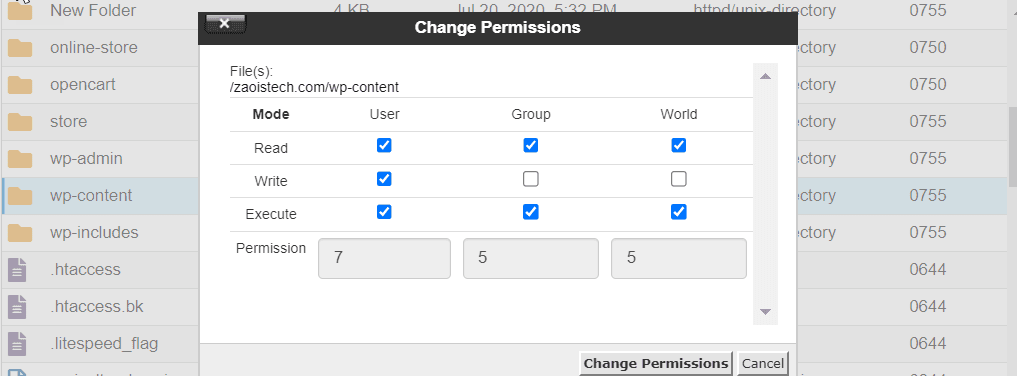
- Check file and folder permissions. Verify and, if needed, rectify file and folder permissions on your web server. Incorrect permissions can render files or folders inaccessible. Use your hosting control panel (e.g., cPanel) to adjust permissions, typically setting folders to 755 and files to 644 for public resources.
- Implement redirects for moved pages. If you have moved or renamed pages with new URLs, set up 301 redirects from the old URLs to the new ones. This ensures that users are redirected to the correct page instead of encountering a 404 error.
- Restore broken links or corrupt files. If you know which pages have broken links, fix them by updating to the correct URLs or setting up appropriate redirects. For missing or corrupt files, restore them from a backup.
- Address permalink issues. In content management systems like WordPress, errors can occur due to permalink or redirect issues. Update permalink settings in your CMS dashboard to resolve site-wide issues.
- Create a custom 404 page. Create a user-friendly custom 404 error page that provides valuable information to visitors encountering the error. This page should include:
- A clear statement explaining the unavailability of the requested resource.
- Guidance for users to check and correct possible errors in the URL.
- Suggestions for verifying the URL’s correctness.
- Top and bottom menus or links to other useful pages on your website.
- A search bar to facilitate in-site searches.
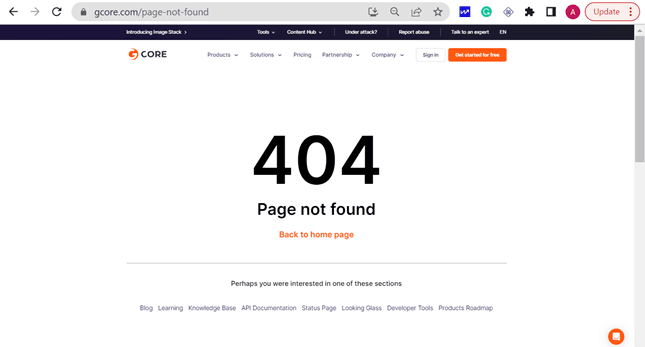
For example, if you request an invalid page from the Gcore website by typing an incorrect URL, you are presented with a custom page informing you that the page cannot be found and presenting options to return to the homepage or explore other sections of the website.
By following the steps and best practices outlined here, you can effectively address Error 404 issues, enhance the user experience, and maintain the functionality of your website. Regular monitoring and proactive error resolution are key to ensuring a seamless browsing experience for your visitors.
Conclusion
Every website or online application has the potential to return Error 404 when a requested page, file, or resource is unavailable. To provide a seamless user experience, monitor and fix issues that could result in Error 404. By customizing your website’s Error 404 page to make it more user-friendly, you can help visitors find the resource or relevant information even if Error 404 occurs.
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.