You may need to determine the distribution version of your operating system if you want to connect third-party repositories or install specific software on a server that was not built and configured by you. In this guide, we will explore three methods to check the version of Ubuntu.
Method #1: Using the command line
1. Connect to the server.
2. Open the terminal window and execute the following command:
lsb_release -aThis command retrieves the release information of your Ubuntu system. Look for the line that starts with “Description” or “Release” in the output.

Note: Ubuntu version numbers follow a pattern of <Year>.<Month>, representing the year and month of the release.
Method #2: Using the command line (alternative)
1. Open the Terminal.
2. Enter the following command:
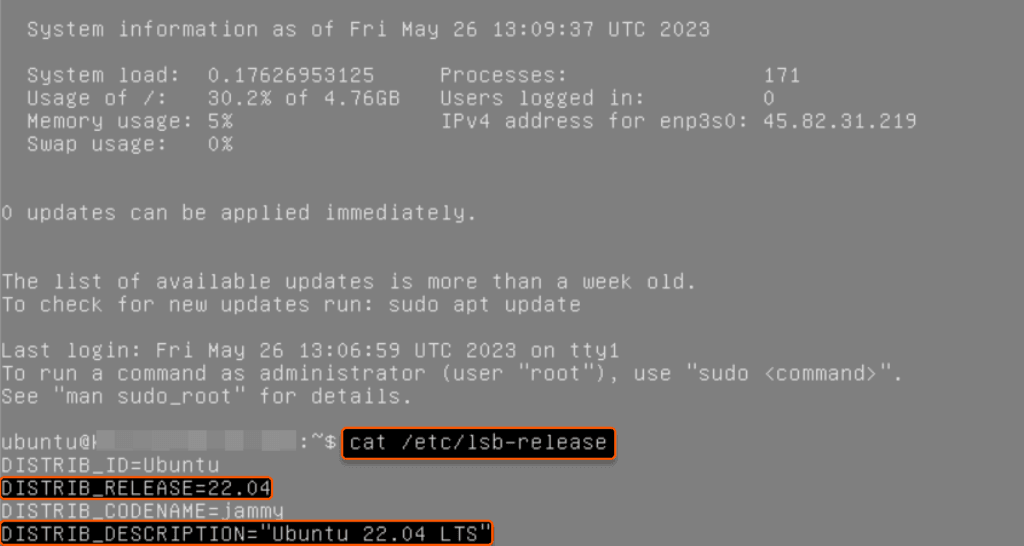
cat /etc/lsb-releaseThis command displays the contents of the “/etc/lsb-release” file, which contains information about your Ubuntu version.
Look for the line starting with “DISTRIB_RELEASE=”. The text after the equals sign (“=”) indicates your Ubuntu version number. Additionally, you can find information about the Ubuntu version on the line “DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION”.
Method #3: Using the system settings
1. Connect to the server where a graphical user interface (GUI) such as GNOME is installed.
2. Search for and open “Settings”.

3. In the “Settings” page, locate the “About” section.
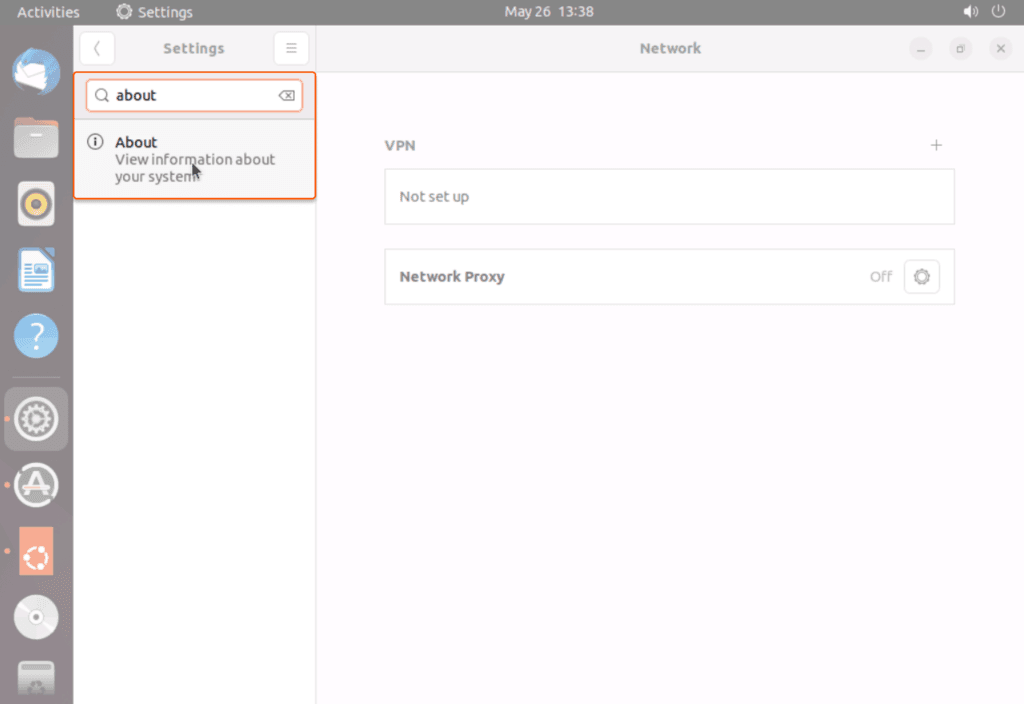
Under the “OS Name” section, you will find your Ubuntu version mentioned.

By following these methods, you can easily check the version of Ubuntu installed on your system.
Conclusion
Want to run Ubuntu in a virtual environment? With Gcore Cloud, you can choose from Basic VM, Virtual Instances, or VPS/VDS suitable for Ubuntu:
- Gcore Basic VM offers shared virtual machines from €3.2 per month
- Virtual Instances are virtual machines with a variety of configurations and an application marketplace
- Virtual Dedicated Servers provide outstanding speed of 200+ Mbps in 20+ global locations
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.