Forgetting a password can be a minor hiccup for most, but when it comes to Linux—a system known for its robust security features—it can feel like a daunting obstacle. Whether you’re new to the world of open-source operating systems or a seasoned Linux veteran, resetting your password doesn’t have to be a complex chore. This guide offers a concise, step-by-step approach to help you swiftly regain access to your Linux machine.
Resetting Linux Password using GRUB
Resetting a Linux password using the GRUB bootloader involves booting into single-user mode or recovery mode and then using the command line to reset the password. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Access the GRUB menu. GRUB (Grand Unified Bootloader) is the default bootloader for most Linux distributions. First, restart or power on your computer. As soon as the boot process begins, press and hold the Shift key (for some systems it might be the Esc key) to bring up the GRUB menu.

2. Enter the Edit Mode. Before booting into the system, you need to edit the boot parameters. First, highlight the default boot entry (usually the first in the list) using arrow keys.
- Press ‘E’ to edit the entry.
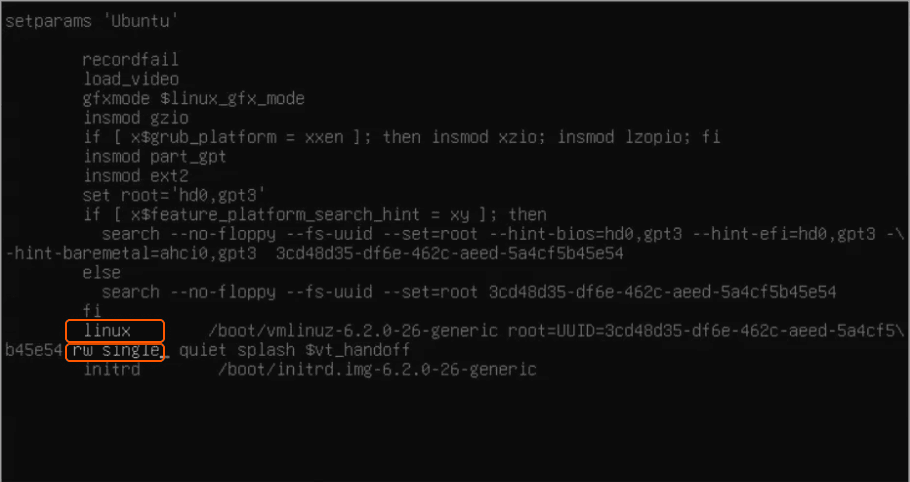
3. Modify Boot Parameters. To boot into single-user mode, you need to modify the Linux boot parameters. Here are the following steps:
• Find the line that starts with linux or linux16. This line specifies the boot parameters.
• At this line, locate ‘ro quiet’, replace ‘ro’ to ‘rw’ then add the word single or init=/bin/bash, depending on your distribution and setup.
• Press Ctrl + X or F10 to boot with the modified parameters.
Here’s an example:
4. Remount the File System with Write Permissions. By default, the filesystem might be in read-only mode in this state. To change the password, you’ll need write permissions. Enter the following command:
mount -n -o remount,rw /5. Reset the Password. Use the passwd command to reset the password for a user. Enter the command below, replacing ‘username’ with the actual username for which you want to reset the password:
passwd usernameWhen prompted, enter the new password twice.

6. Reboot the System. Now that the password is reset, it’s best to reboot the system to return to normal operation. Enter the following command:
syncThen, force a reboot with:
reboot -fThe new password should now be active, and you can test it. In the following section, we’ll explore an alternative method using a live CD or USB.
Resetting Linux Password Using Live CD/USB
Resetting a Linux password using a Live CD or USB is a useful method when you’ve forgotten the root or user password. Here are the step-by-step instructions:
1. Boot from the Live CD/USB. Insert your Live CD or USB stick. Reboot the computer and choose to boot from the CD/USB from the BIOS or UEFI boot menu.
2. Open a Terminal. Once the live environment is loaded, locate and open a terminal window.
3. Identify the System’s Root Partition. You can use tools like fdisk or lsblk to identify your system’s root partition.
sudo fdisk -l# orsudo lsblk -fLook for partitions that are likely Linux root partitions, such as ext4, xfs, etc.
4. Mount the Root Partition. Create a mount point by running this command:
sudo mkdir /mnt/myrootMount the identified root partition (replace /dev/sdXY with your partition, for example, /dev/sda1):
sudo mount /dev/sdXY /mnt/myroot5. Change Root into the System. Use chroot to change the root directory by using this command:
sudo chroot /mnt/myroot6. Reset the Password. Now that you’ve chrooted into your system, you can use the passwd command to change the password for any user, including root.
passwd usernameReplace “username” with the actual username or use root to reset the root password.
7. Exit and Unmount. Exit the chroot environment and unmount the partition.
exitsudo umount /mnt/myroot8. Reboot. Remove the Live CD/USB and reboot your computer. Now, you should now be able to log in using the new password.
That’s it! You’re now able to reset passwords in Linux. To reset passwords, you can use either the GRUB method or a Live CD. The GRUB method is fast and doesn’t need external tools, but a Live CD is more universal and works well for complex system setups or restricted GRUB access.
Conclusion
Looking to deploy Linux in the cloud? With Gcore Cloud, you can choose from Basic VM, Virtual Instances, or VPS/VDS suitable for Linux:
- Gcore Basic VM offers shared virtual machines from €3.2 per month
- Virtual Instances are virtual machines with a variety of configurations and an application marketplace
- Virtual Dedicated Servers provide outstanding speed of 200+ Mbps in 20+ global locations
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.