When you visit a website or load an app, you expect it to work, and fast. But how does that content reach you from halfway across the world almost instantly?
One reason is a behind-the-scenes technology, a network addressing and routing methodology called Anycast. If you're choosing a CDN or DNS hosting service provider, it's worth understanding what Anycast does because it can significantly improve your customers’ experience of your online services and content by speeding up loading, reducing downtime, and providing more consistent performance.
What is Anycast?
Anycast is a network routing method where multiple servers in different locations share the same IP address. When a user sends a request, it’s routed to the closest server based on network path efficiency.
Think of it like calling a customer service number and getting routed to the closest available agent. If one agent is unavailable, the call goes to the next-closest one. You can also compare it to a car GPS. If a road is closed, you get rerouted and still arrive at your destination smoothly.
How Anycast benefits your customers
Anycast can be used with CDN and DNS services. With a CDN, Anycast ensures that content will be served to eyeballs from the closest point of presence. This improves speed and reliability.
The overall benefits to your customers are significant:
- Faster load speed: With Anycast, users connect to the nearest available server. This reduces round-trip time and latency, improving load speed.
- Less downtime: If one server fails, traffic is automatically rerouted to the next available node. This boosts availability, minimizing downtime. In addition, having multiple routes available means no single point of failure. If one path is unavailable, another is used, thanks to Anycast’s redundancy.
- Consistent performance: Anycast’s load distribution helps balance traffic across multiple servers, especially during traffic spikes. That means great performance even at peak times.
- Better DDoS resilience: Anycast helps absorb distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks by spreading incoming traffic across multiple points of presence. This makes it harder for attackers to overwhelm a single server. At Gcore, we use Anycast to power Super Transit for superior DDoS protection.
How it works behind the scenes
Anycast routes user requests to the nearest server that shares a common IP address, using a protocol called BGP (Border Gateway Protocol). Each server advertises the same IP, and BGP determines the optimal route based on routing policies and network topology, not just physical distance.
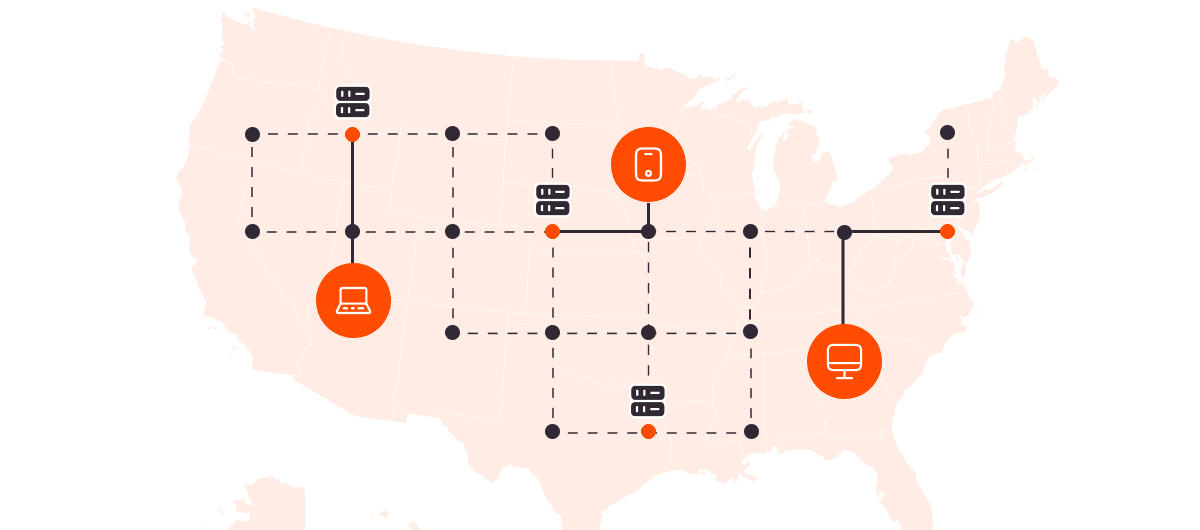
If a server goes offline, BGP stops advertising it. The request is automatically routed to the next-best server.
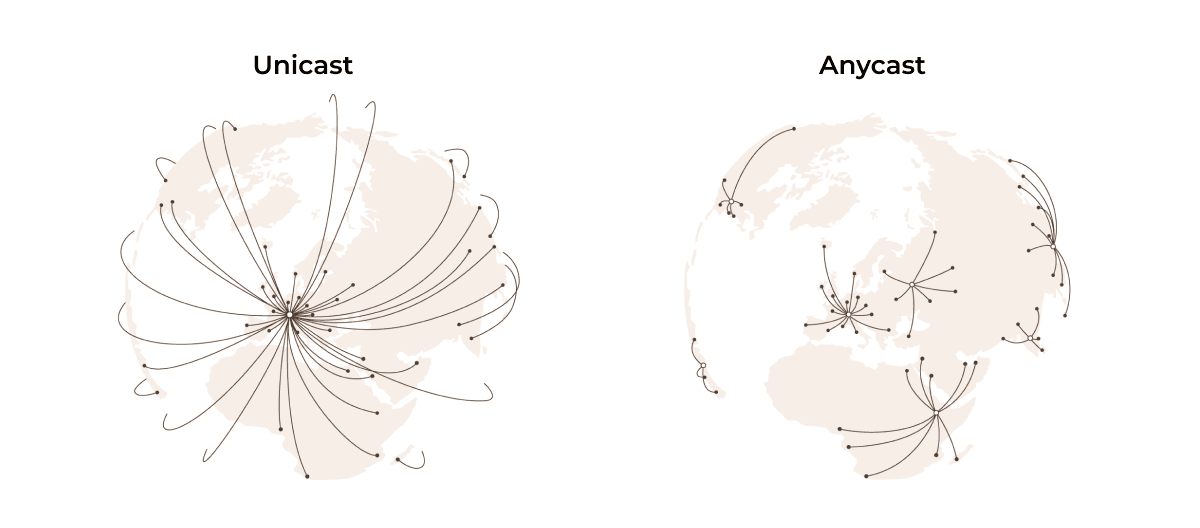
The alternative to Anycast is Unicast. Unicast assigns one IP address to one server, so all traffic is routed to that single location, no matter where the user is.
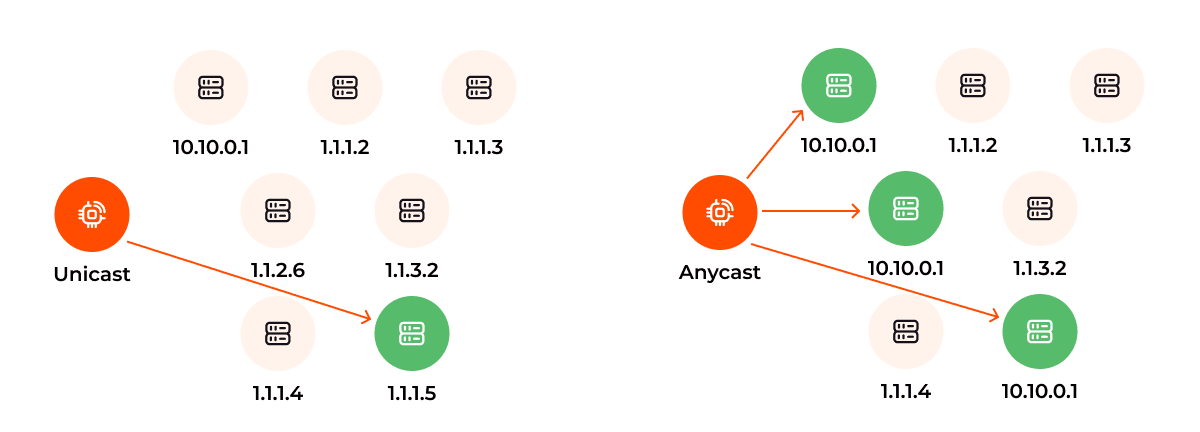
That means in a Unicast setup, users in Asia may still connect to a server in Europe, slowing down load times. With Anycast, users in Asia would connect to a server in Asia for faster responses.
Limitations of Anycast
Anycast isn’t always the best choice for every workload. Real-time applications like voice calls, video conferencing, or financial transactions that depend on long-lived, stateful connections can sometimes experience disruptions if routing changes mid-session.
And failover isn’t instant. When a server fails, BGP may take several seconds to re-converge and reroute traffic. This can briefly affect availability, though it is still significantly faster than manual failover processes.
That said, these risks can often be mitigated. Many platforms design their applications to re-establish sessions quickly or use protocols that tolerate reconnections. Where strict session persistence is essential, you can combine Anycast with additional logic or fallback mechanisms.
Gcore’s implementation is flexible. DNS-based Anycast is enabled by default, but you can fine-tune traffic behavior and routing policies depending on your setup and use cases. Our team is available 24/7 to advise on best practices for applications that may be sensitive to routing changes.
Gcore and Anycast
Anycast is a core part of Gcore CDN and DNS infrastructure. Our global network is designed to maximize its impact, delivering faster responses, higher reliability, and better protection for your services. This also improves our FastEdge and Inference at the Edge availability and latency.
Key capabilities include:
- 210+ points of presence worldwide for broad coverage and regional performance
- 20ms average global latency for consistently fast response times
- Real-time failover to keep services available even during outages
- Intelligent traffic distribution to balance load and prevent congestion
With Gcore, wherever your users are, they can connect quickly and reliably.
Experience Anycast with Gcore today on our free-forever CDN plan. Or, if you’re looking for a CDN provider, check out our free ebook on how to choose a CDN provider.
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.