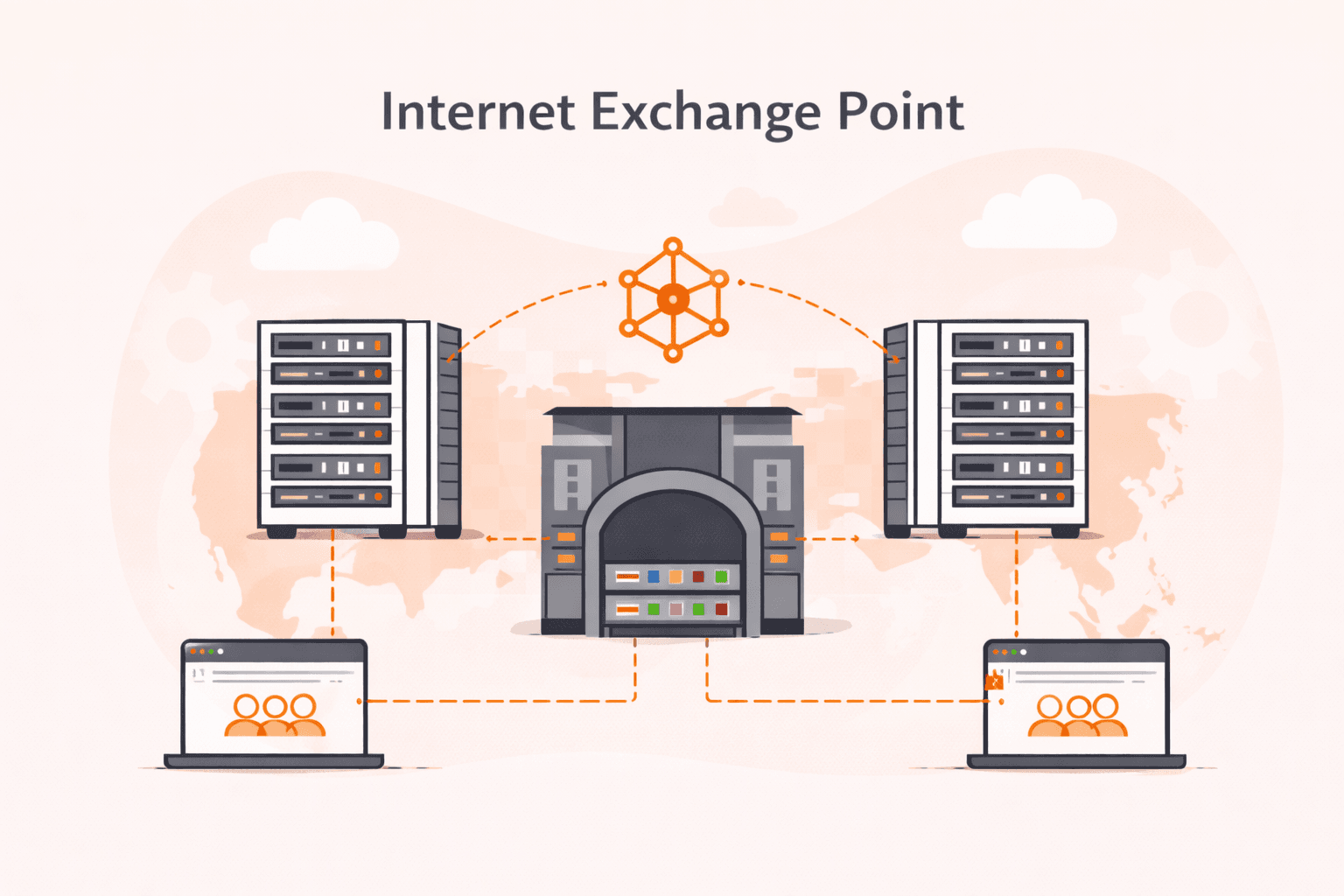
Developers
Discover the latest industry trends, get ahead with cutting‑edge insights, and be in the know about the newest Gcore innovations.
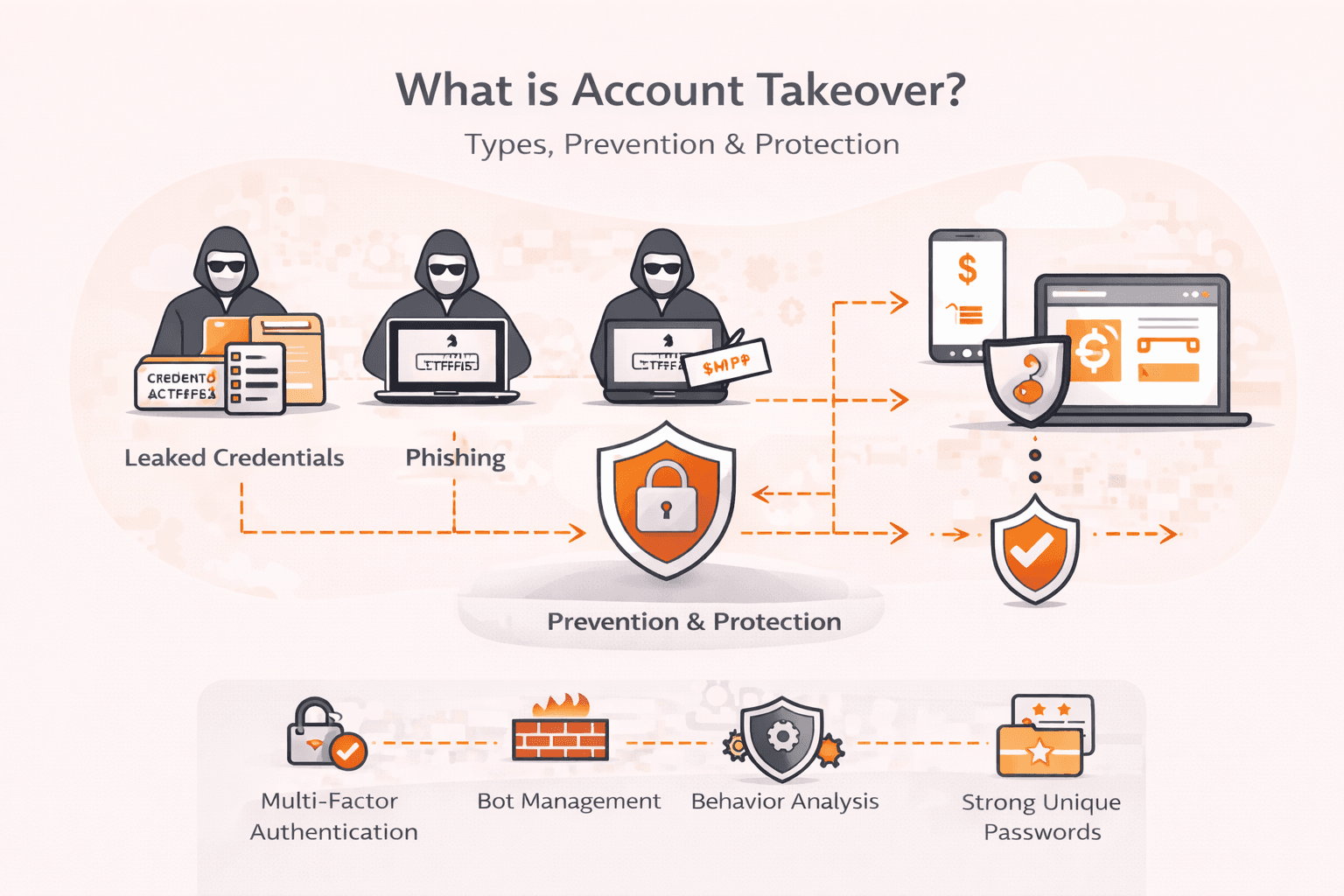
Your CFO's email account gets compromised overnight. By morning, cybercriminals have downloaded client banking information, stolen sensitive financial data, and grabbed credentials to your company's bank accounts. This isn't hypothetical, i
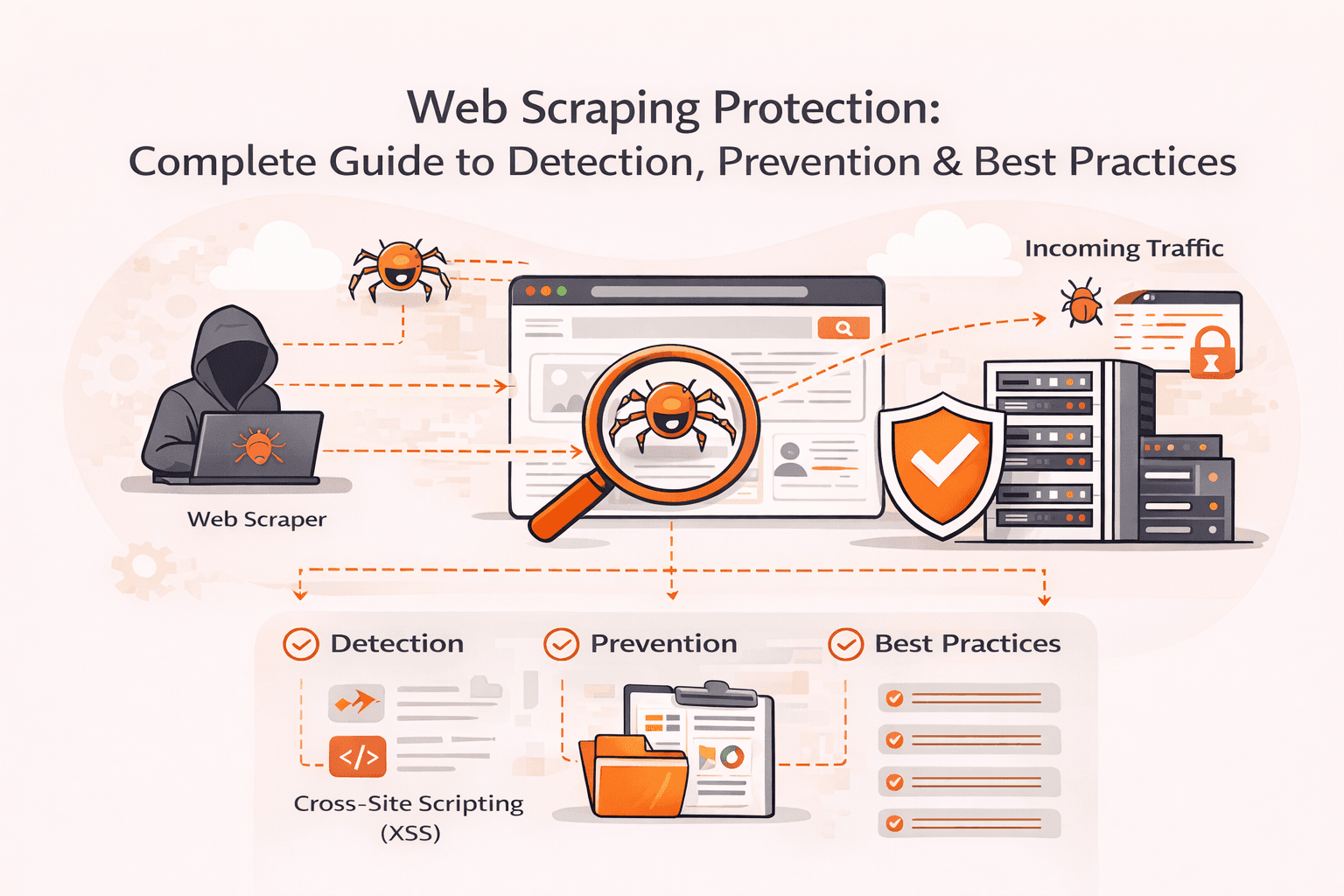
Your server load suddenly spikes by 400%. Legitimate customers can't access your site. Competitors are methodically copying your product descriptions, pricing data, and proprietary content. Modern scraping bots are draining your resources a
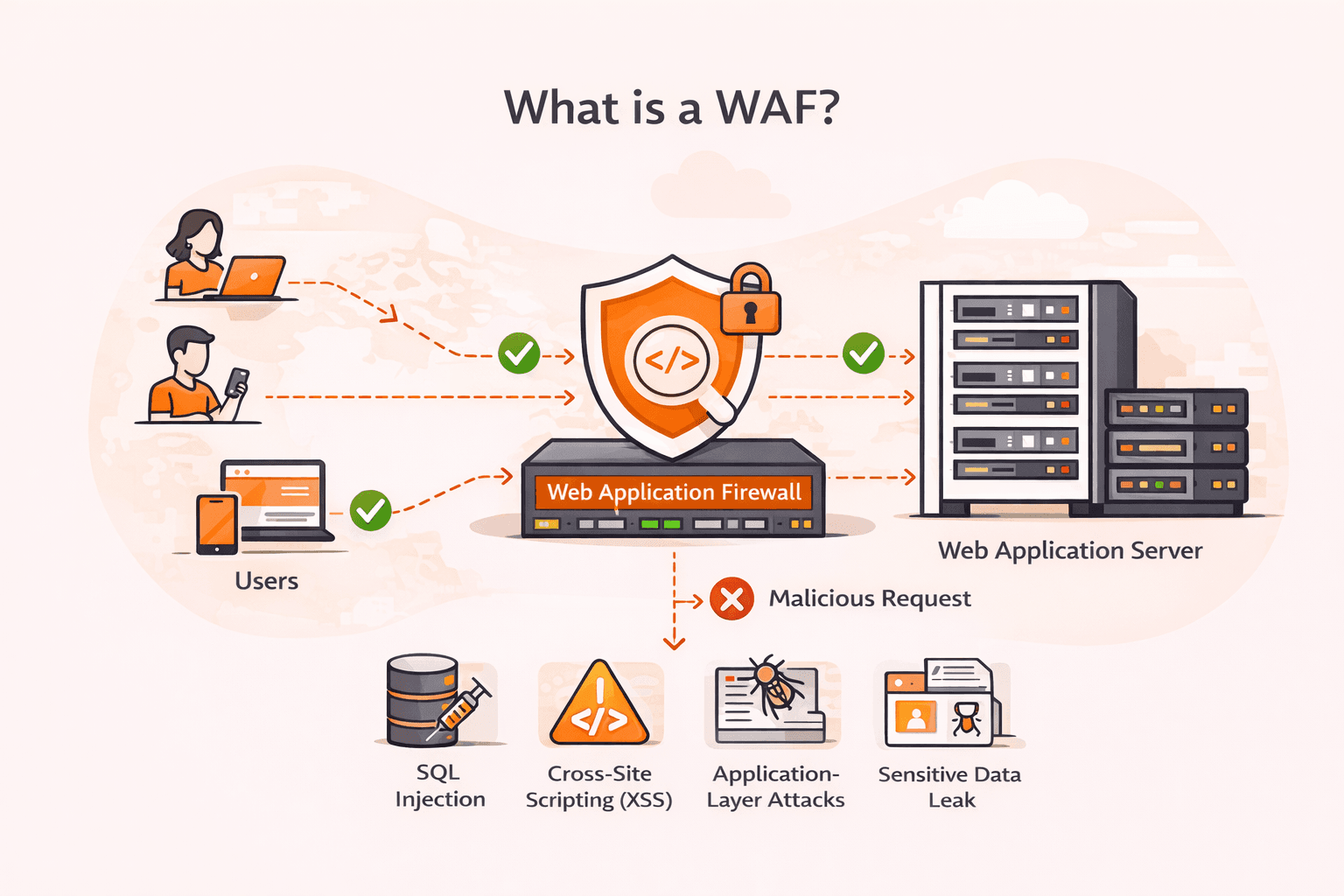
Your web application just processed what looked like a normal login request, but it was actually an SQL injection attack that exposed your entire customer database. Cross-site scripting (XSS), SQL injection, and other application-layer atta
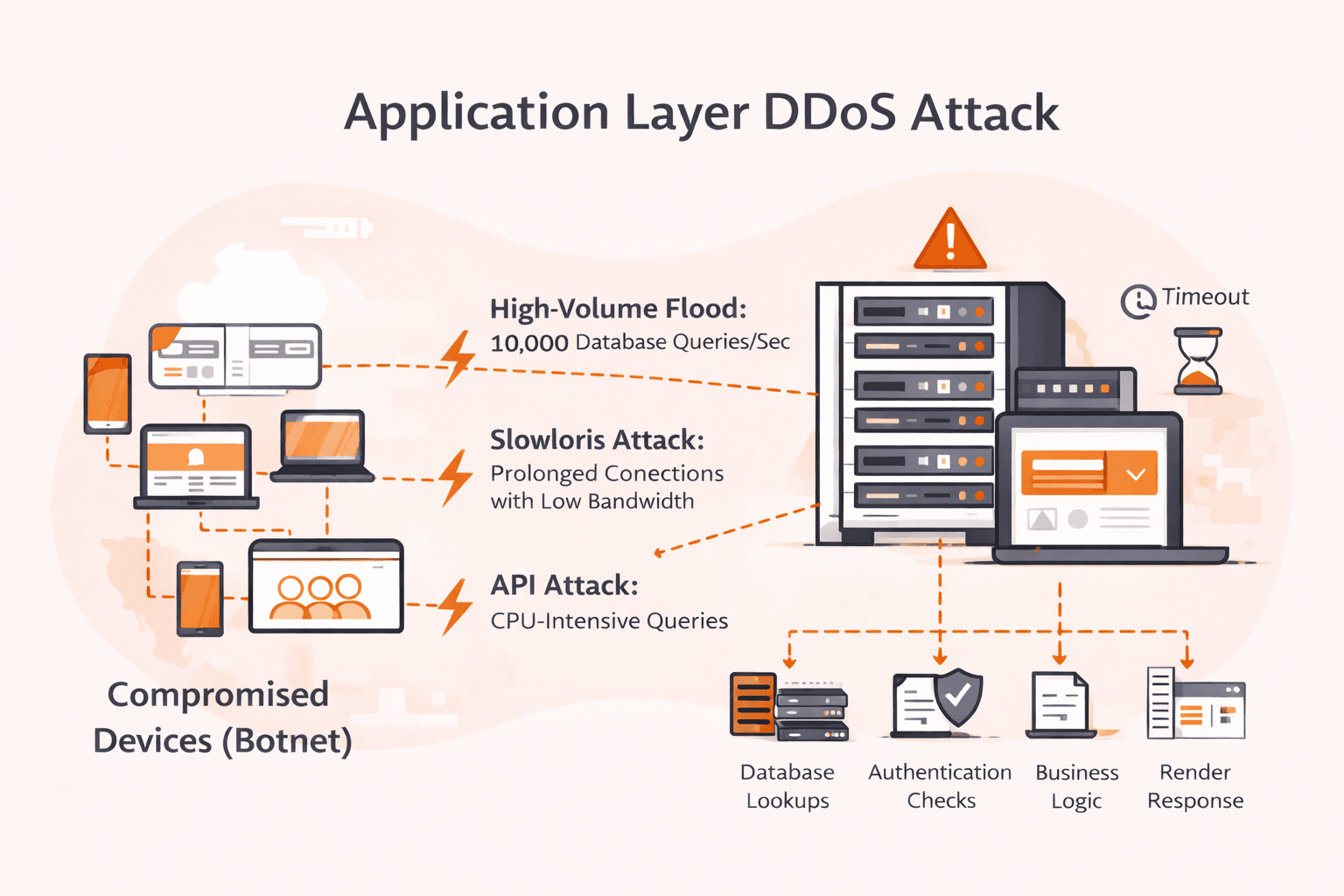
Your network dashboards show green. Bandwidth utilization is at 5%. Yet your application is dying, response times spike to 30 seconds, users get timeout errors, and your on-call engineer can't figure out why. Welcome to application layer DD
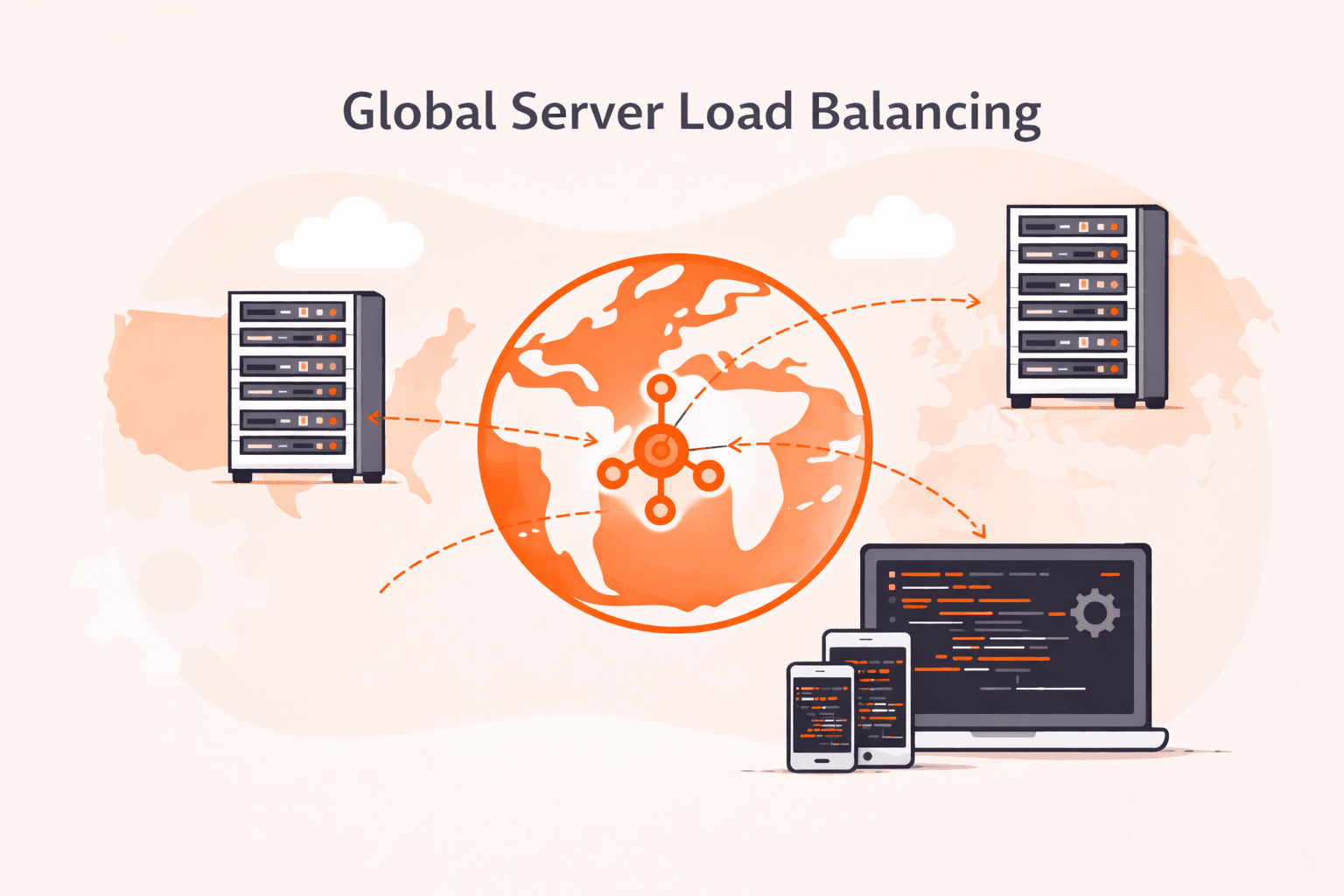
Global server load balancing is a traffic management system that distributes user requests across servers in multiple geographic locations to improve performance and reliability. This approach can reduce latency by 40-60% compared to single
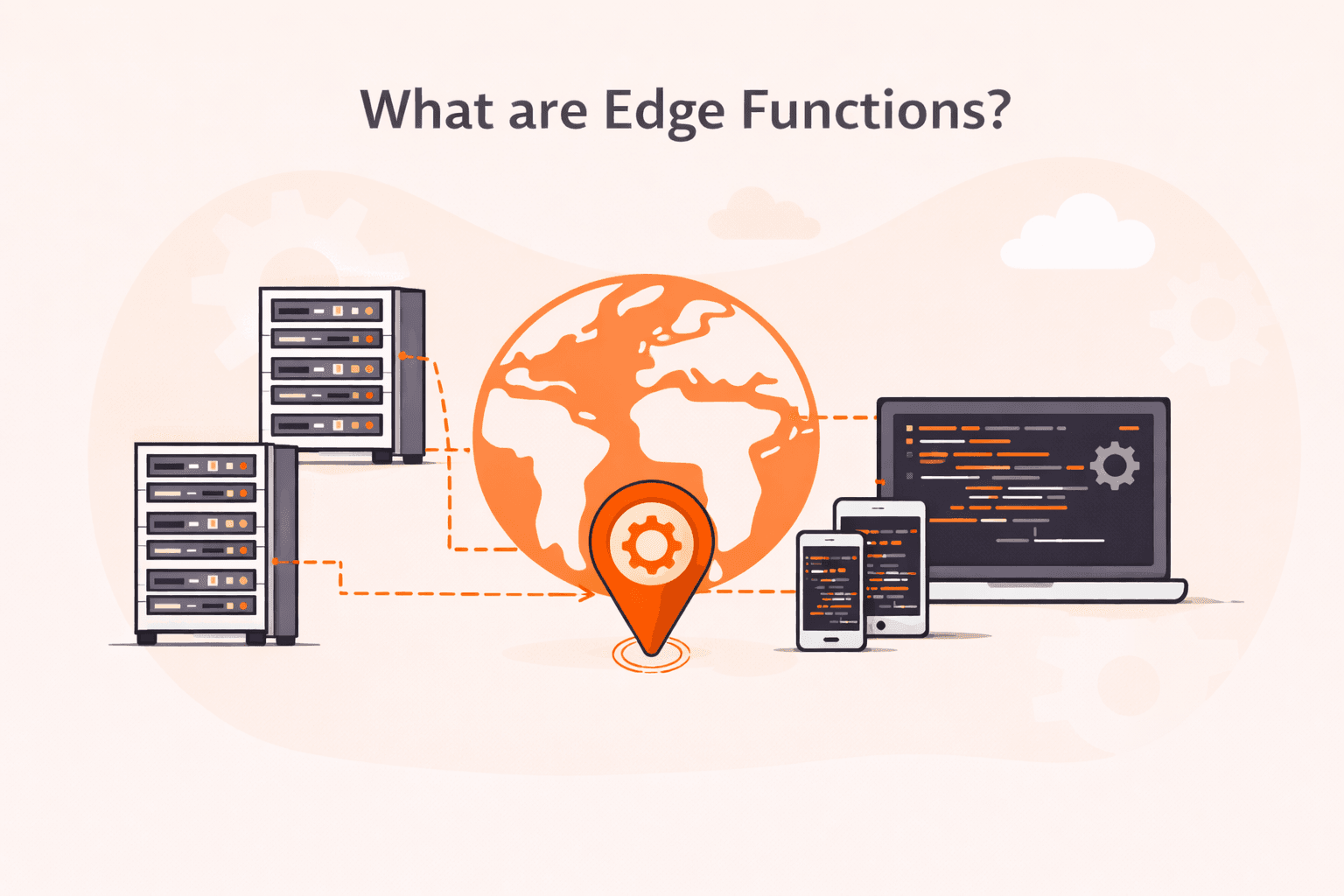
When you're building a web application, there's a good chance you've faced this problem: your server sits in one location, but your users are scattered across the globe. That means someone in Tokyo waits longer for a response than someone i

Most websites today use HTTPS. In fact, 68% of the top million websites have made the switch. But if you're using a CDN to speed up content delivery, SSL/TLS encryption works differently than you might expect. Your origin server isn't handl

Health check monitoring is a systematic process that tracks the availability and performance of your servers, applications, and infrastructure by sending automated requests at regular intervals. Most systems run checks every 30 to 60 second
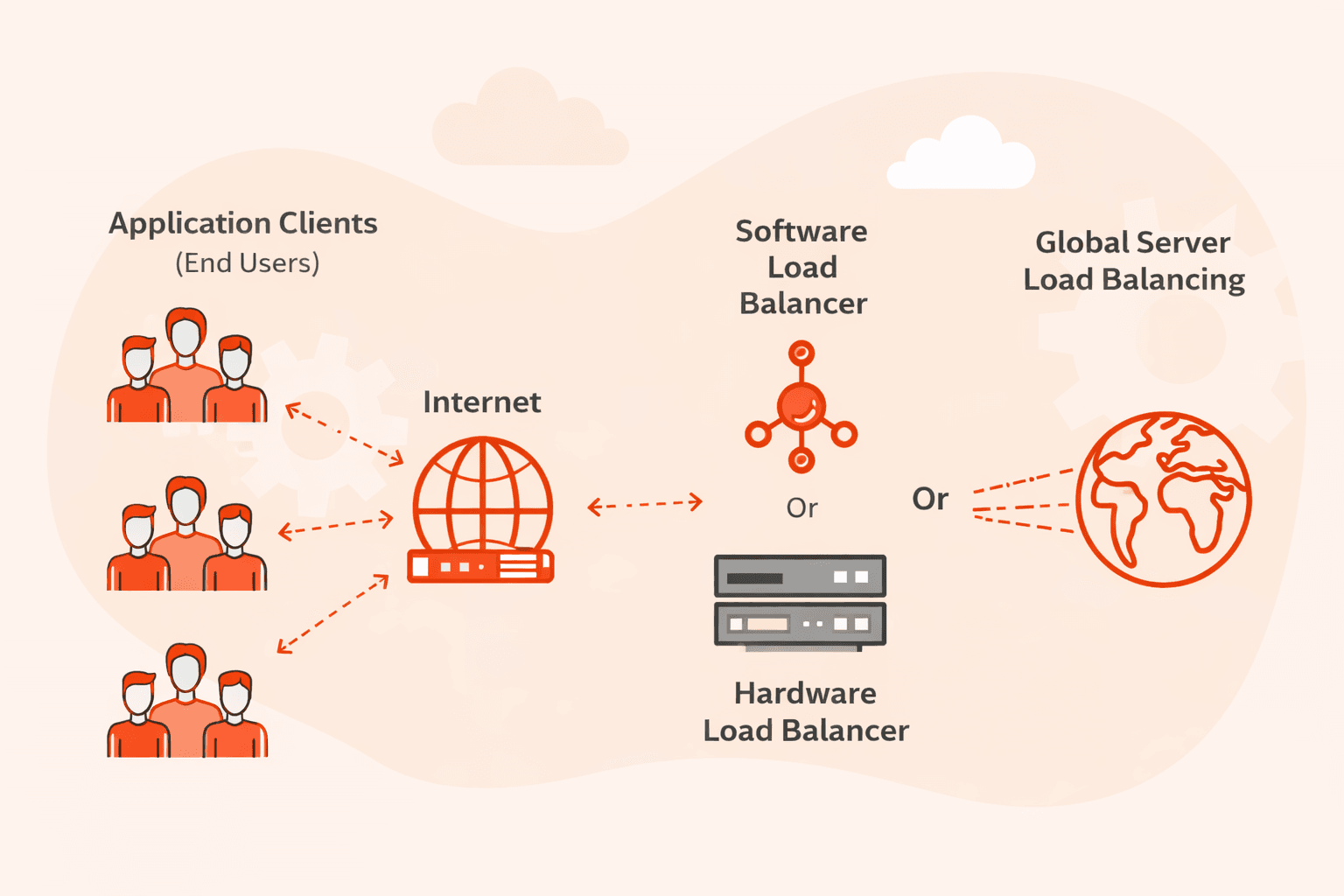
GSLB (Global Server Load Balancing) is a load balancing service that distributes client requests across multiple geographically dispersed data centers to improve performance, availability, and compliance.At its core, GSLB works at the DNS l
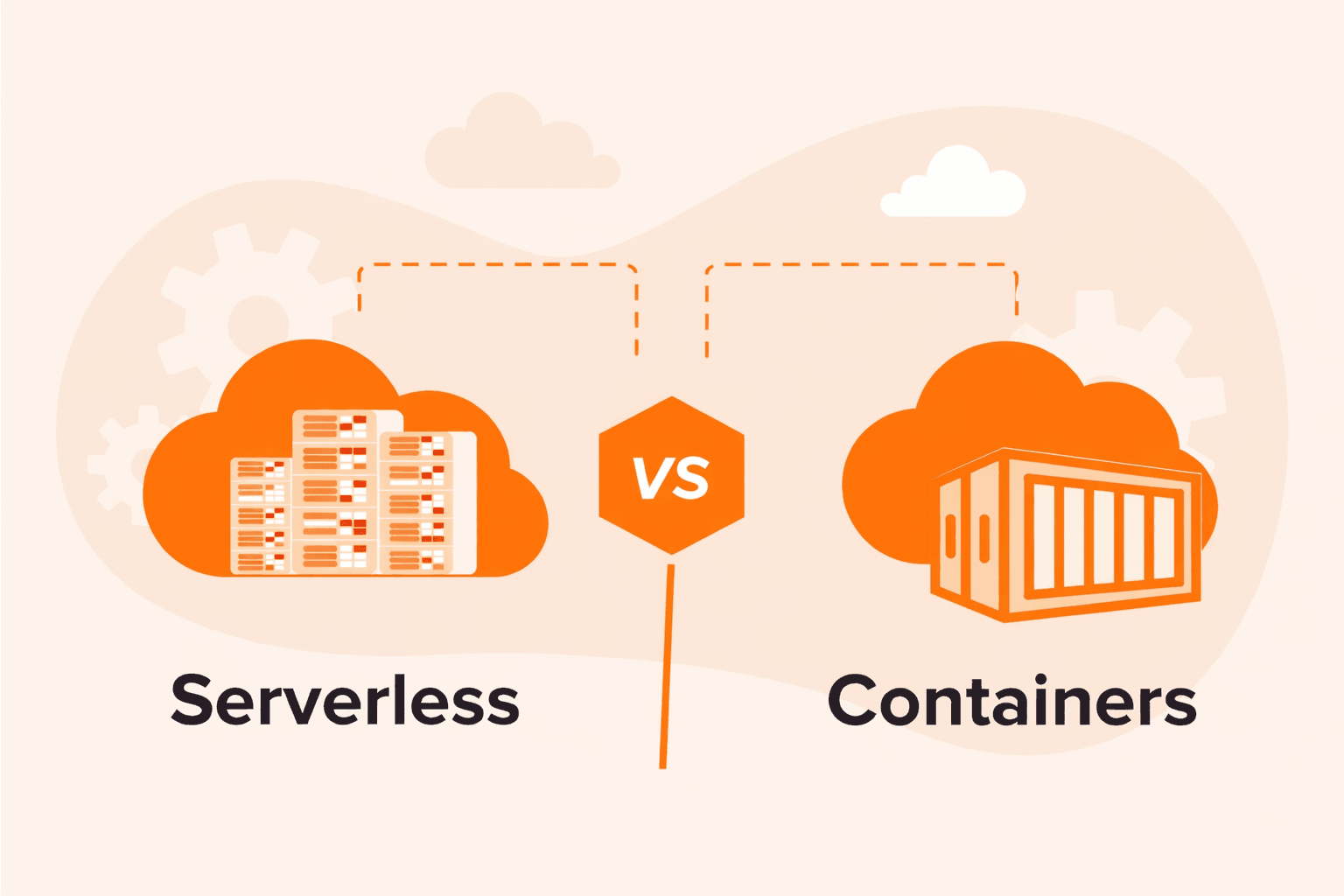
Building modern applications means making a fundamental choice: serverless or containers?This decision affects how you use code, manage resources, and pay for infrastructure. Here's what you need to know.Serverless computing lets you write
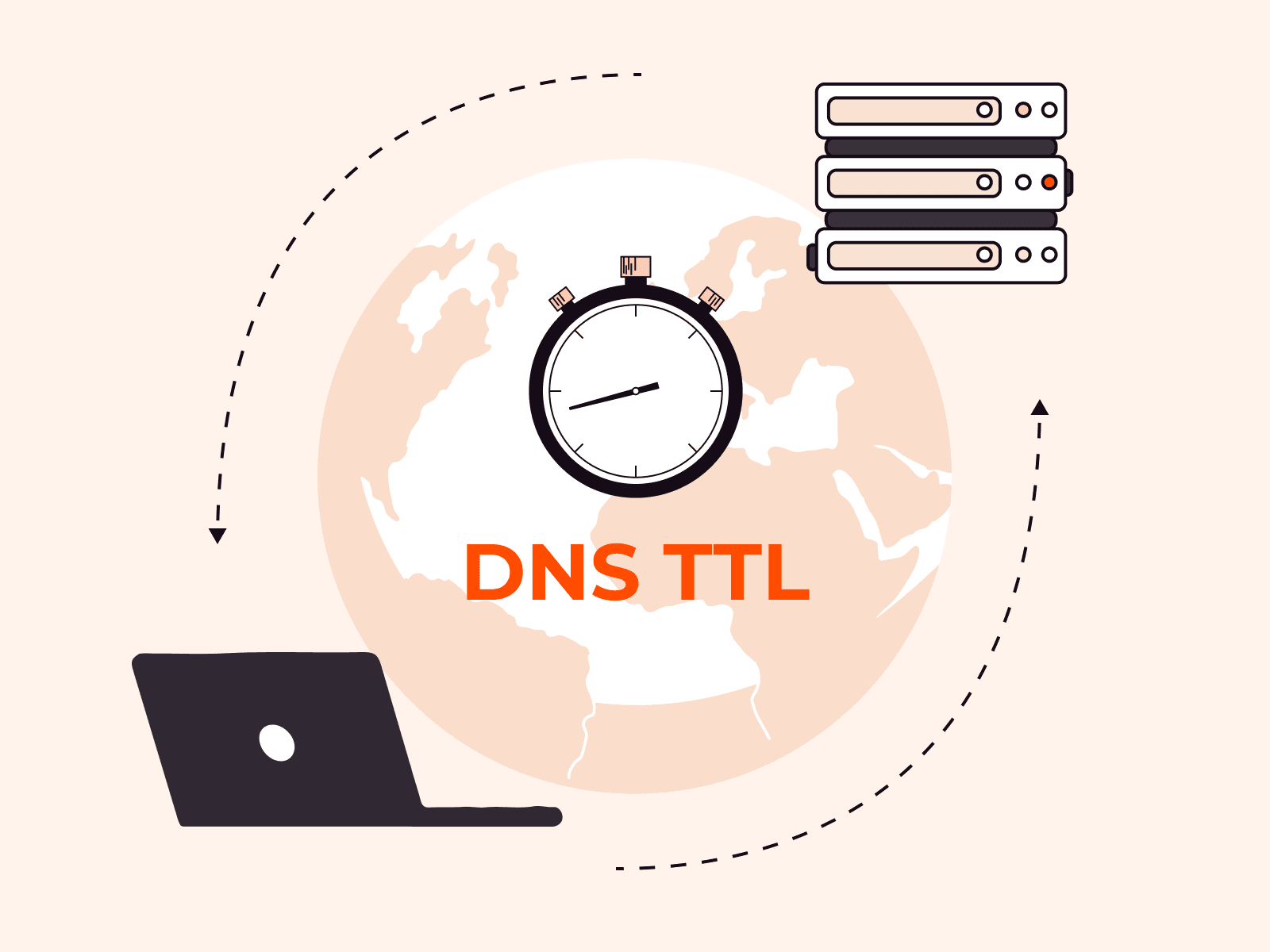
A Domain Name System Time to Live (DNS TTL) is a timer measured in seconds, that determines how long a DNS record stays cached before resolvers must refresh it from the authoritative nameserver.DNS TTL controls caching behavior across the g
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.