For Ubuntu users, having VLC is synonymous with an enhanced media experience, free from the constraints of format incompatibilities. This guide delves into the seamless process of installing VLC on Ubuntu, ensuring you’re just a few clicks away from a world-class multimedia playback experience.
What is VLC?
VLC, or VLC Media Player, is a free and open-source, cross-platform multimedia player and framework. It’s developed by the VideoLAN project and has garnered popularity due to several notable features:
- Broad Media Format Support. VLC can play a vast array of multimedia formats, effortlessly handling MP3, MP4, MKV, AVI, MOV, OGG, FLAC, and many others. It can also play DVDs, audio CDs, VCDs, and various streaming protocols without the need for external codecs.
- Compatibility. VLC is available for a plethora of platforms, from Windows, macOS, and Linux to mobile ecosystems like Android and iOS.
- No Need for Additional Codecs. VLC’s comprehensive codec support ensures smooth playback of nearly all multimedia files right out of the box, eliminating the hassle of downloading extra codec packs.
- Advanced Features. Beyond mere playback, VLC offers tools for media conversion, streaming capabilities, and even video effects and adjustments.
- Community Support. With its open-source ethos, VLC boasts a vibrant community, ensuring its evolution with regular updates, fixes, and improvements based on genuine user feedback.
Installing VLC on Ubuntu
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to install VLC on Ubuntu:
1. Update the Package Index. Begin by ensuring your package list and software are up to date.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y2. Install VLC. Now, install VLC using the apt package manager.
sudo apt install vlcIf that doesn’t work, you can also try these following commands:
sudo snap install vlc sudo apt install vlc-binExample:
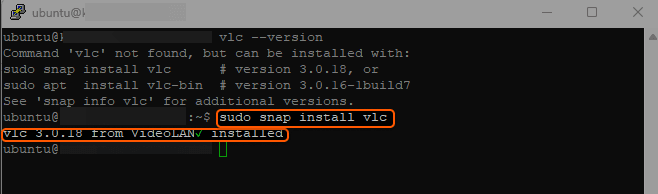
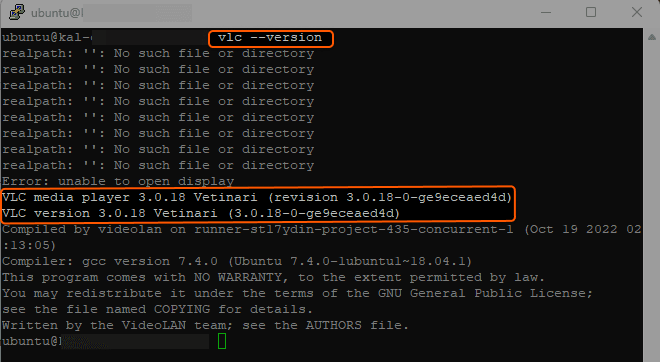
3. Verify Installation. Once installed, you can check the version of VLC to verify it was installed correctly.
vlc --versionExample:
4. Launch VLC. You can now launch VLC either from the terminal or through the Ubuntu application menu.
vlcExpected Output: VLC Media Player will open and show its familiar user interface.
That’s it! You’ve successfully installed VLC on Ubuntu. Whenever you want to play media files, VLC will be ready to handle almost any format you throw at it.
Conclusion
Want to run Ubuntu in a virtual environment? With Gcore Cloud, you can choose from Basic VM, Virtual Instances, or VPS/VDS suitable for Ubuntu:
- Gcore Basic VM offers shared virtual machines from €3.2 per month
- Virtual Instances are virtual machines with a variety of configurations and an application marketplace
- Virtual Dedicated Servers provide outstanding speed of 200+ Mbps in 20+ global locations
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.