In today’s connected world, service uptime is crucial. Whether you’re managing a personal project or an enterprise-level application, interruptions can be costly and troublesome. This article provides you with a comprehensive guide to ensuring that vital Linux services bounce back swiftly from any hiccups, reducing downtime and streamlining system management. Dive in to discover practical steps for setting up your Linux system to handle unexpected service terminations gracefully.
Restarting a Linux Service
1. Access the Service File. First, you’ll need to locate the service’s unit file. This is usually found in /etc/systemd/system/ or /lib/systemd/system/.
cd /etc/systemd/system/Another option is using this command:
cd /lib/systemd/system/2. Edit the Service File. Use your preferred text editor (like nano or vim) to edit the service file. For this example, let’s assume the service is named example.service.
sudo nano example.serviceSample output:
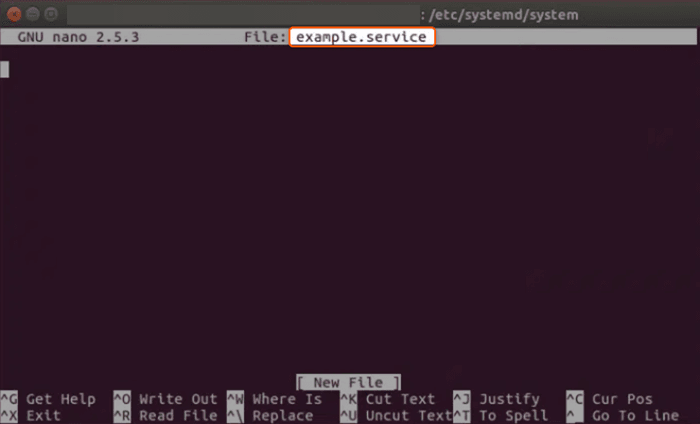
3. Modify the [Service] Section. Find the [Service] section in the service file, and add or modify the following lines:
Restart=alwaysRestartSec=3- Restart=always. This Ensures that the service will always restart, no matter how it was stopped or crashed.
- RestartSec=3. This ensures that the service will wait for 3 seconds before it restarts. This can be adjusted based on your needs.
4. Save and Close. Save the file and exit the text editor. If you’re using nano, press CTRL + X followed by Y (to confirm saving) and then press Enter.
5. Reload systemd. For systemd to recognize the changes you made to the service file, you need to reload its configuration:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload6. Test the Configuration. Stop the service and observe if it restarts automatically.
sudo systemctl stop example.serviceAfter a few seconds (based on the RestartSec value you set), the service should restart itself.
7. Enable the Service. If you want your service to start on boot and utilize the auto-restart feature.
sudo systemctl enable example.serviceThat’s it! You’ve successfully set up your Linux service to restart automatically. Regularly monitoring logs and service statuses will ensure that everything runs smoothly.
Conclusion
Looking to deploy Linux in the cloud? With Gcore Cloud, you can choose from Basic VM, Virtual Instances, or VPS/VDS suitable for Linux:
- Gcore Basic VM offers shared virtual machines from €3.2 per month
- Virtual Instances are virtual machines with a variety of configurations and an application marketplace
- Virtual Dedicated Servers provide outstanding speed of 200+ Mbps in 20+ global locations
Related articles
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get the latest industry trends, exclusive insights, and Gcore updates delivered straight to your inbox.