In the complex ecosystem of a Linux system, understanding the processes that run in the background is crucial for effective system management and troubleshooting. Whether you’re a system administrator wanting to monitor system health, or an everyday user curious about what’s running under the hood, this guide will walk you through the different methods for listing running processes on Linux. With practical steps and useful tips, we’ll help you gain a comprehensive view of your system’s activity.
Benefits of Viewing Running Processes in Linux
Running processes in Linux underpins the functionality of the operating system and offers various advantages. Here are five key benefits
- Multitasking Capability. Linux allows multiple processes to run concurrently. This means that a user can simultaneously execute various applications, such as browsing the web while listening to music, without causing interference between them.
- Resource Efficiency. Linux efficiently allocates system resources among running processes. The OS employs sophisticated scheduling algorithms to ensure that high-priority tasks receive more CPU time, while lower-priority tasks don’t hog resources.
- Process Isolation. Each process in Linux operates within its own memory space, which means that one process cannot directly interfere with or crash another. This enhances system stability and security.
- Fine-grained Control. With tools like ps, top, and htop, Linux users and administrators can monitor, prioritize, or even terminate processes. This provides a high level of control over system resources and application behavior.
- Flexibility for Developers. Linux provides a rich set of system calls and tools for process management. Developers can spawn, control, and terminate processes programmatically, leading to the development of robust and efficient applications and services.
How to View Running Processes in Linux
Let’s delve into the process of viewing running tasks on a Linux system. Here’s the guide below:
#1 Open the Terminal
Open your terminal by either searching for “Terminal” from the application menu or pressing Ctrl + Alt + T simultaneously.
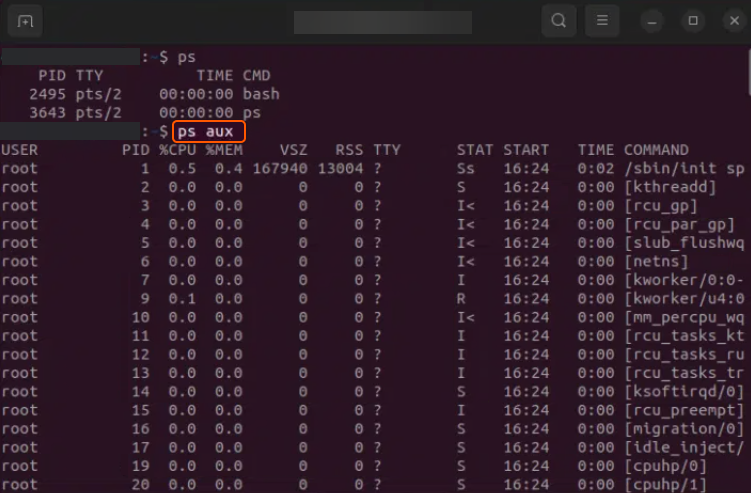
#2 Use the ps Command
This command provides information about the currently running processes:
ps
This command, by default, will display processes running in the current shell. To view all the processes:
ps aux
For aux:
- a. lists processes from all users
- u. displays the process’s user/owner.
- x. lists processes not attached to a terminal.
Sample Output:
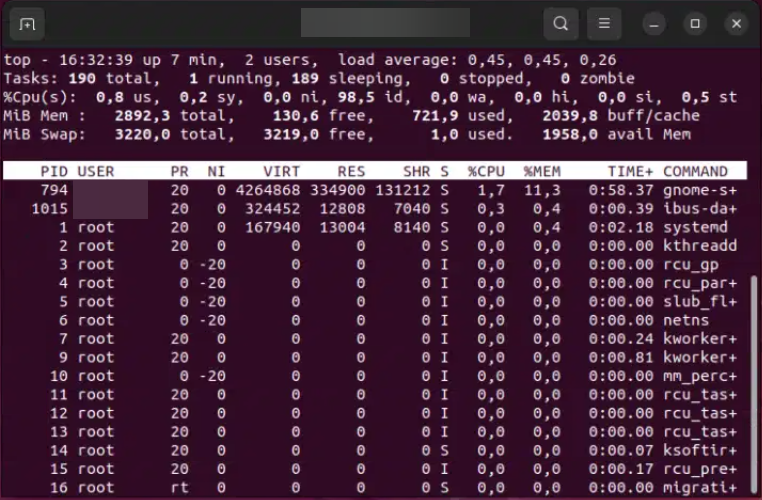
#3 Use the top Command
This command provides a dynamic, real-time view of running processes.
top
You’ll see an interactive screen that refreshes periodically. This tool lists processes in descending order of CPU usage.
Sample Output:
#4 Use the htop Command
htop is an enhanced version of top with a more user-friendly interface and added features. It might not be pre-installed on all Linux distributions. To install, run this command.
sudo apt-get install htop # For Debian-based systems like Ubuntu sudo yum install htop # For RedHat-based systems like CentOS
Then, run this command below.
htop
#5 Search for a Specific Process
If you want to find a specific process, you can use grep along with ps:
ps aux | grep [process-name]
Replace [process-name] with the name or part of the name of the process you’re searching for. After you’ve completed your tasks, you can now close the terminal.
Well done! You can now successfully view running processes in Linux. This guide has provided you with a basic grasp of this capability. However, remember that Linux offers a variety of other advanced tools and commands for those seeking more detailed insights and greater control over system processes.
Conclusion
Looking to deploy Linux in the cloud? With Gcore Cloud, you can choose from Basic VM, Virtual Instances, or VPS/VDS suitable for Linux:
- Gcore Basic VM offers shared virtual machines from €3.2 per month
- Virtual Instances are virtual machines with a variety of configurations and an application marketplace
- Virtual Dedicated Servers provide outstanding speed of 200+ Mbps in 20+ global locations