The Linux Time Command is a useful tool for measuring command performance in the Linux operating system. It provides insights into system efficiency and allows users to understand how different tasks affect their system. Whether you’re new to Linux or just looking to understand your computer better, this friendly guide will walk you through what the time command is and how you can use it. It’s a handy little trick to have up your sleeve!
Linux Time Command and Usage
The Linux time command is a tool used in the Linux operating system to measure how long a particular command takes to execute. It’s often used by developers, system administrators, or anyone looking to analyze the performance of a process or a script.
Here’s how it works:
#1 Command Line Usage
The Linux time command is used to determine the duration of a particular command or program’s execution. The basic syntax for the time command is as follows:
time [options] command [arguments]
- ‘time’: The command itself, used to initiate the time tracking.
- ‘[options]’: These are optional flags that can modify the behavior of the time command. For example, the -p option can be used to display the output in a portable POSIX format.
- ‘command‘: The specific command or script you want to measure.
- ‘[arguments]’: Any arguments or parameters that the specified command might require.
Here’s a basic example using the time command with the ls command:
time ls -l
This will run the ls -l command, which lists files in long format, and then display how long it took to execute.
The time command measures how long a command takes to run. Specific options vary depending on the system and version of time installed. Here are some common options.
| -p | Produce output in a format that’s compatible with POSIX |
| -o FILE, –output=FILE | Direct the command’s output to a file. |
| -a, –append | Append the results to the file instead of overwriting, if used with -o. |
| -f FORMAT, –format=FORMAT | Define a custom format for the output. |
| –verbose | Provide more detailed output. |
| –quiet | Suppress the command’s error output. |
| –portability | Similar to -p, for portable output format. |
There are many more placeholders you can use to customize the output. You can find the full list in the time command’s man page, accessible by running:
man time
Here’s a sample output of “man time” command:
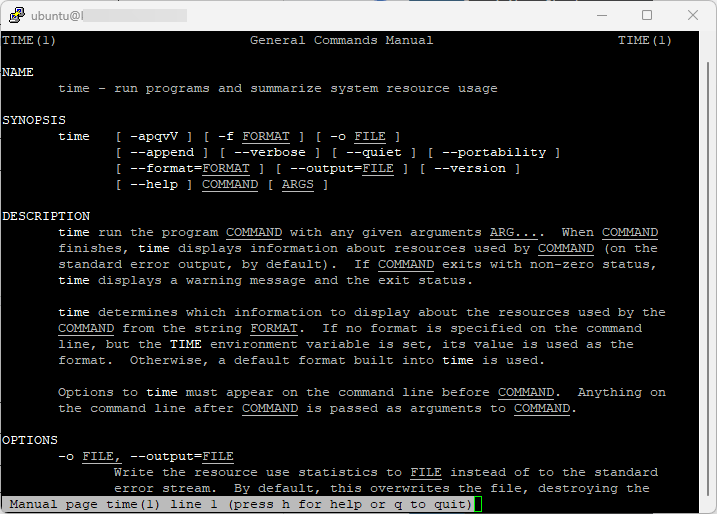
#2 Syntax Time Command Output
The output typically consists of three lines showing the real time, user time, and system time.
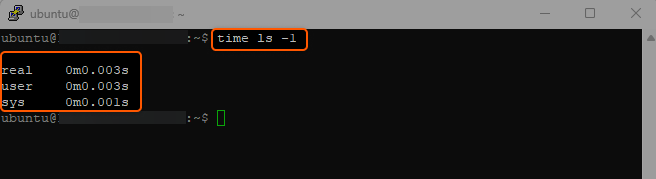
- Real Time (real). The actual time it took to execute the command, from start to finish.
- User Time (user). The time the CPU spent on the task itself.
- System Time (sys). The time the CPU spent on system-level tasks related to the command.
Grasping the Linux Time commands lets you observe how a command functions with the system, identifying possible slowdowns or problems with performance.
The Linux time command serves as a robust instrument for those aiming to comprehend the effectiveness of their programming or the conduct of their system. It offers in-depth awareness of how the computer’s resources are being employed.
Conclusion
Looking to deploy Linux in the cloud? With Gcore Cloud, you can choose from Basic VM, Virtual Instances, or VPS/VDS suitable for Linux:
- Gcore Basic VM offers shared virtual machines from €3.2 per month
- Virtual Instances are virtual machines with a variety of configurations and an application marketplace
- Virtual Dedicated Servers provide outstanding speed of 200+ Mbps in 20+ global locations