
In this article, we will discuss how to set up Odoo on an Ubuntu server using a Docker image. As a sample server, we will deploy a Gcore Basic instance, a low-cost virtual machine that saves you time and effort; you can have a server ready in just five minutes! Then we will install Docker on this server and run Odoo.
You don’t need much experience with Ubuntu and Docker administration to get Odoo up and running. Just follow the recommendations and CLI commands we provide here.
What Is Odoo?
Odoo is an open-source business management software that offers a huge variety of modules, such as accounting, inventory, and sales. Odoo Community is available for free, without time and user number limits.
How to Install and Run Odoo
Step 1. Prepare a Virtual Machine for your Odoo Server
As mentioned above, we will run Odoo on a Gcore Basics instance. Here are the steps:
- Log in to your Gcore Cloud account. If you don’t have one yet, sign up.
- Go to Cloud and select Projects.
- Click Create project; fill in the Name field. Projects are groups of separate Cloud resources, and these groups are isolated from each other. The isolation gives you the ability to set user rights for each project.
- In your project, click Create Instance.
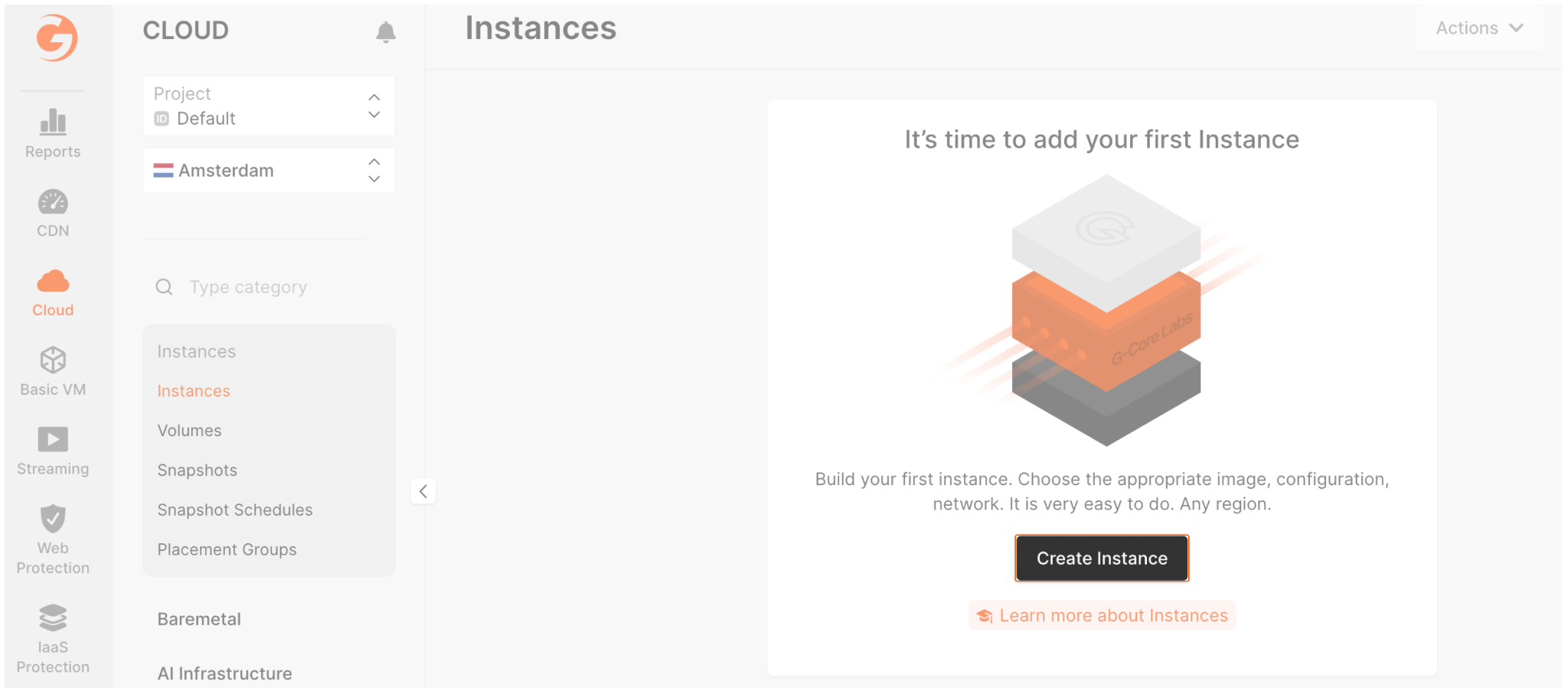
- Select the region closest to your location from the available options: Amsterdam (EU), Frankfurt (EU), Manassas (US), Tokyo (Japan), or Hong Kong (China.)
- In Image, select Distributions and set the following parameters:
- OS: Ubuntu 22.10.
- Type: Basic VM.
- Flavor: 1 vCPU / 2GB RAM / 25GB SSD.
- Network: set by default with public IP.
- Firewall: select “Default” with the “Add application ports to firewall group” flag.
- SSH Key: choose your public SSH key or generate a new one.
- Name: odoo-server (or whatever you want.)
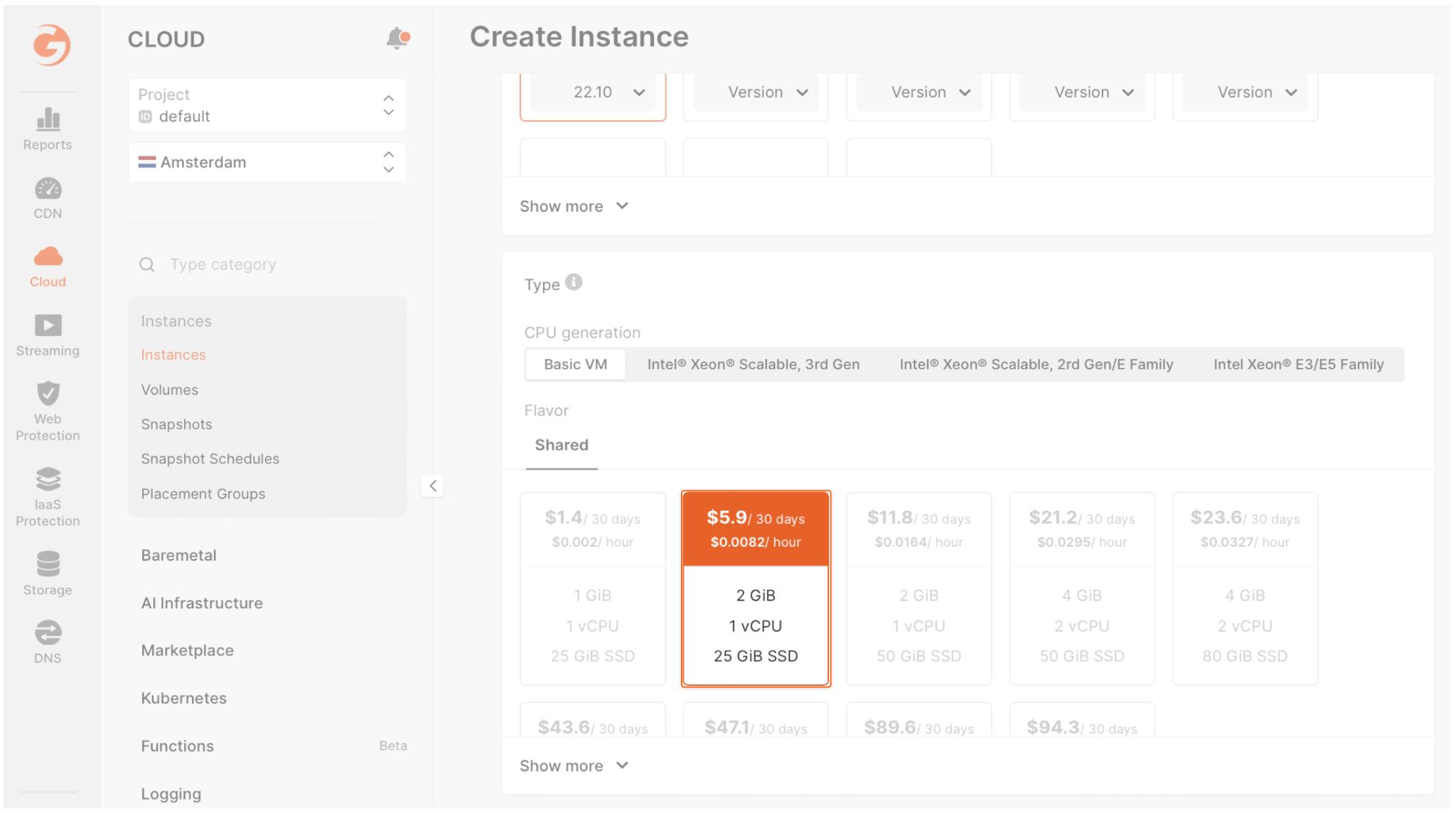
- Now that you’ve finished the set up, click Create Instance. The virtual machine will appear in the “Instances” list. Wait until the virtual machine’s “Creating” status changes to “Power on.”
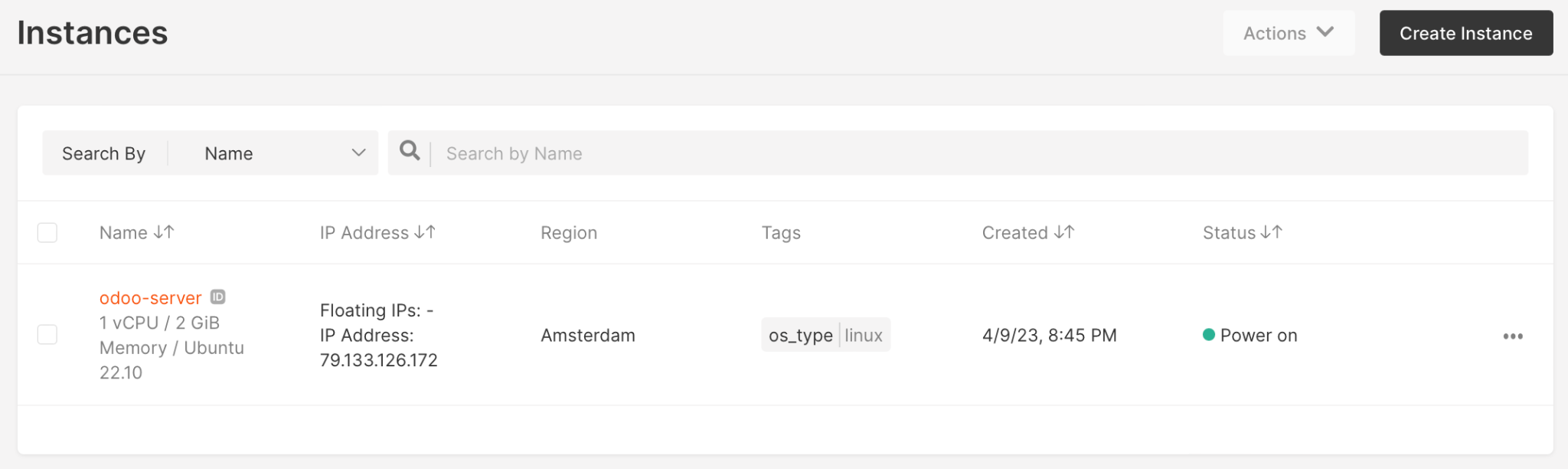
Step 2. Connect to a Server and Update Ubuntu
Before installing Docker and Odoo, make sure that the Ubuntu OS is up to date.
- Log in to the server by SSH using the following command:
ssh ubuntu@<your_public_ip_address>
For example:
ssh ubuntu@79.133.126.172
- Update Ubuntu:
ubuntu@odoo-server:~$ sudo su root@odoo-server:/home/ubuntu# apt update
Step 3. Install Docker
To install Docker, run the following command:
root@odoo-server:/home/ubuntu# apt install docker.io
Step 4. Run the Odoo Server with PostgreSQL in Docker
Odoo uses PostgreSQL as an internal database. For Odoo to work properly, you need to run the PostgreSQL server as well. To do so, use the following commands:
root@odoo-server:/home/ubuntu# docker run -d -e POSTGRES_USER=odoo -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=odoo -e POSTGRES_DB=postgres --name db postgres:15 root@odoo-server:/home/ubuntu# docker run -p 8069:8069 --name odoo --link db:db -t odoo
Step 5. Add the Inbound Rule 8069 in the Firewall
The Odoo server uses port 8069 as a default for HTTP connections. Add the inbound rule for this port to the firewall:
- Go to the Networking → Firewall and select the default firewall group.
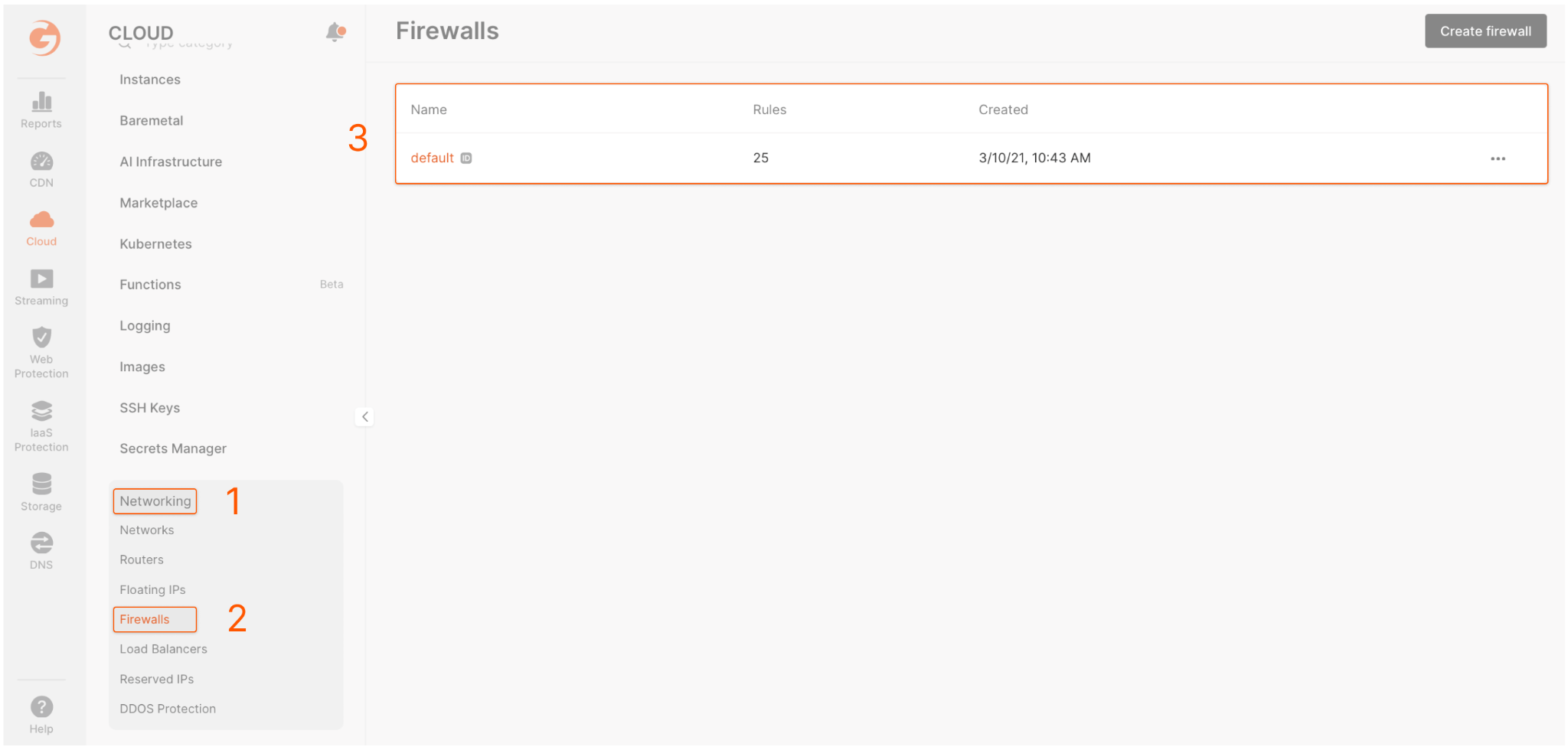
- Click on the default firewall group and set the following parameters:
- Type: Custom
- Protocol: TCP
- Port: 8069
- Sources: All IPv4
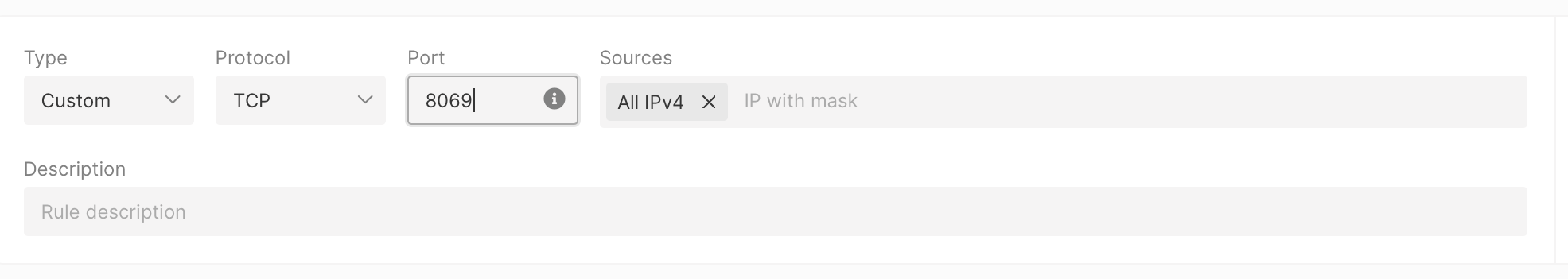
- In the lower-left corner of the “Firewalls” section, click Save.
Note: You also can configure this rule using one command in CLI (it works for any virtual machine, not only for Gcore’s):
sudo ufw allow 8069/TCP
Step 6. Run Odoo
To access the Odoo, open a web browser on your device and enter the public IP address of your Odoo server that you obtained in Step 1, as well as the 8069 port:
http://<your_public_ip_address>: 8069
For example:
http://79.133.126.172: 8069
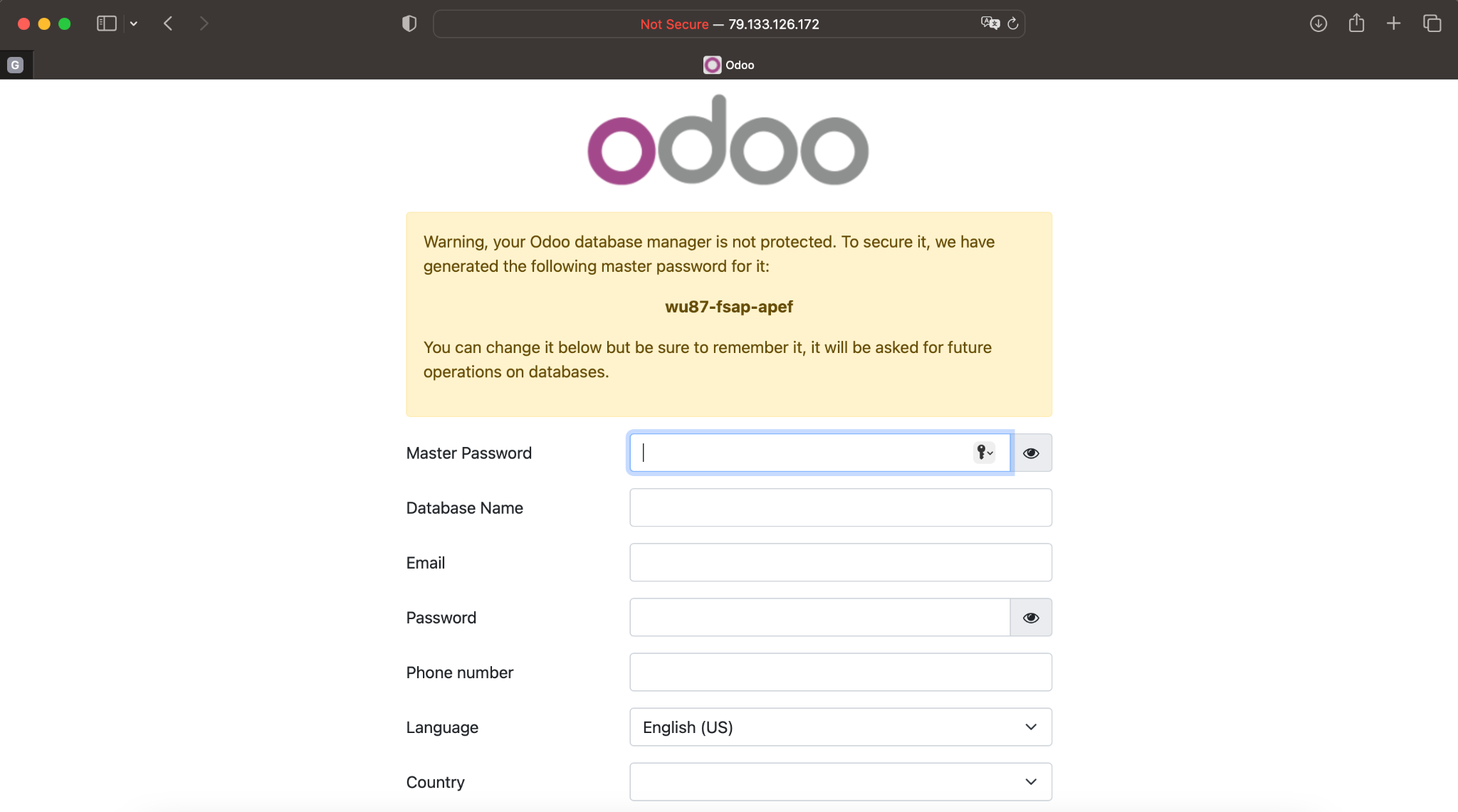
Congratulations! You have successfully set up Odoo on Ubuntu.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we explained how to set up Odoo on an Ubuntu server using Docker image. Check out our other articles dedicated to setting up different types of software on Gcore Cloud instances:






