In the realm of Linux systems, knowing how to determine the Linux directory size holds significant importance for effective storage management. This article serves as a comprehensive guide, leading you through the steps to effortlessly measure the size of a directory in Linux. Explore these methods to optimize your resource utilization and ensure efficient storage practices.
What is Linux Directory?
In Linux, a directory is a file that serves as a container for other files and subdirectories. It acts as a way to organize and structure the file system, allowing users to store and manage files hierarchically. Directories provide a structured way to group related files together, making locating and managing them easier. They are an essential part of the file system’s organization and are crucial in maintaining order and accessibility to files on a Linux system. In the upcoming section, let’s delve into the process of determining the size of a Linux directory.
Determining Directory Size in Linux
Knowing how to determine the size of a directory in Linux is a valuable skill for effective storage management and resource optimization. Whether you’re assessing specific folder space or preventing storage issues, understanding this process is essential. In this guide, we’ll walk you through various methods and commands to accurately calculate directory sizes in a Linux environment.
#1 Using the du Command
Using the ‘du’ command, you can easily determine the size of a directory by displaying the disk space used by files and directories. The output can be customized to be presented in human-readable formats like kilobytes, megabytes or gigabytes.
- Specific folder. To get the size of a specific directory, open your terminal and type the following command.
du -sh /path/to/directory
In this command, replace /path/to/directory with the actual path of the directory you want to assess. The -s flag stands for “summary” and will only display the total size of the specified directory. The -h flag makes the output human-readable, showing sizes in a more understandable format.
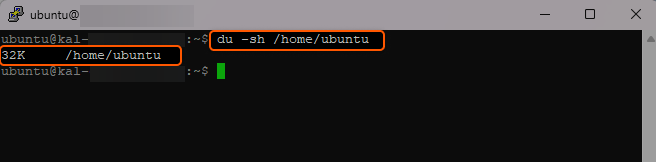
Example. Here, we utilized the path “/home/ubuntu/” (where “ubuntu” is the name of our username directory) and used the “du” command to retrieve an output of 32K for this directory, indicating a size of 32 kilobytes.
- All folders. To get the size of all files and directories within the current directory. Use this command.
sudo du -h /path/to/directory
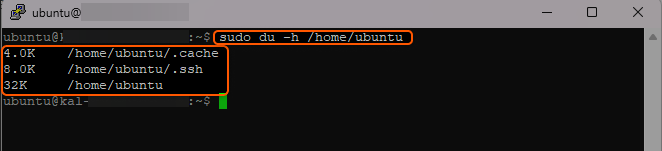
Example. In this instance, we once again utilized the path “/home/ubuntu” (with “ubuntu” representing our username directory). Using the command “du -h,” we obtained an output listing all files and directories within that particular path.
#2 Using the ncdu Tool
If you’re looking for a more interactive and feature-rich approach to explore directory sizes, consider using the ‘ncdu’ (NCurses Disk Usage) tool. ‘ncdu’ provides a visual representation of disk usage and allows you to navigate through directories, viewing size details and identifying large files with ease. For Debian/Ubuntu, use this command:
sudo apt-get install ncdu
Once installed, run ‘ncdu’ followed by the path to the directory you want to analyze.
ncdu /path/to/directory
This will launch the ‘ncdu’ interface, showing a breakdown of sizes for files and subdirectories. Use the arrow keys to navigate and explore various folders, and press ‘q’ to exit the tool.
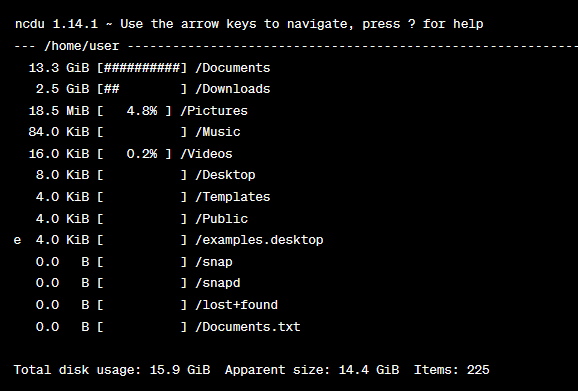
Example. Here’s a sample output of using the ncdu command to analyze the home directory. To do this, simply enter the ncdu command and press Enter. The displayed output will resemble the following:
That’s it! You can now determine the size of a directory in Linux. Measuring directory sizes is a crucial skill for efficient storage management. Whether you choose the straightforward ‘du’ command or utilize the visual advantages of the ‘ncdu’ tool, this expertise enhances your ability to uphold an organized and efficient Linux environment.
Conclusion
Looking to deploy Linux in the cloud? With Gcore Cloud, you can choose from Basic VM, Virtual Instances, or VPS/VDS suitable for Linux:
- Gcore Basic VM offers shared virtual machines from €3.2 per month
- Virtual Instances are virtual machines with a variety of configurations and an application marketplace
- Virtual Dedicated Servers provide outstanding speed of 200+ Mbps in 20+ global locations